Figure 2.
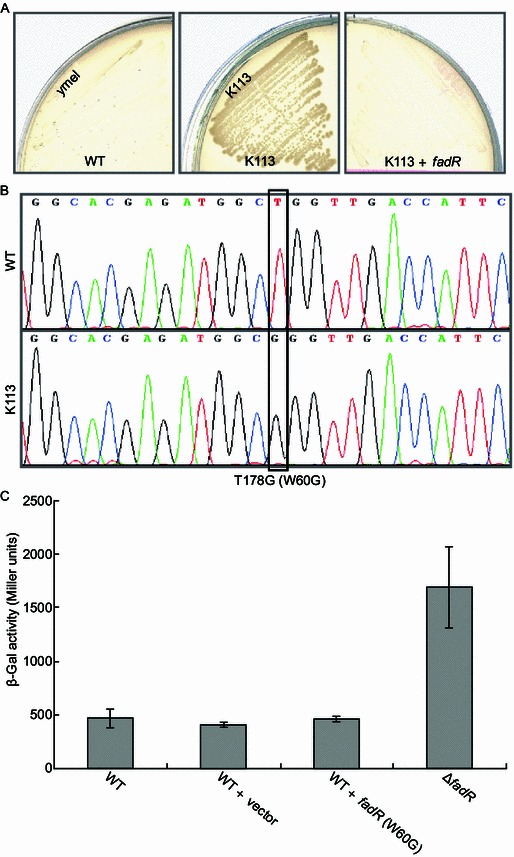
Determination of a single recessive mutation (W60G) present infadRmutant strain K113. (A) Growth phenotype of E. coli fadR mutant strain K113 on minimal media with C10 as sole carbon source in comparison with those of the wild-type strain and the fadR complemented strain. The three strains used here included WT (ymel strain) (Feng & Cronan, 2009a), K113 (fadR mutant) (Feng & Cronan, 2009a, Clark et al., 1983) and the complemented strain FYJ7 (K113, zcf-117::Tn10, fadR+, TetR) (Feng & Cronan, 2009a). (B) A single mutation (T178G) present in the K113 fadR revealed by direct DNA sequencing. The mutation of T178G at DNA level denotes the mutation of at protein level. (C) The mutation of W60G in FadR is genetically recessive. β-Gal activities were recorded in three independent experiments. All the strains assayed here contain a chromosomal fadBA-lacZ transcriptional fusion (Table 1). They are SI203 (WT), SI207 (ΔfadR), FYJ225 (WT + vector) and FYJ226 (WT + fadR (W60G)), respectively. Vector: pBAD24
