Figure 4.
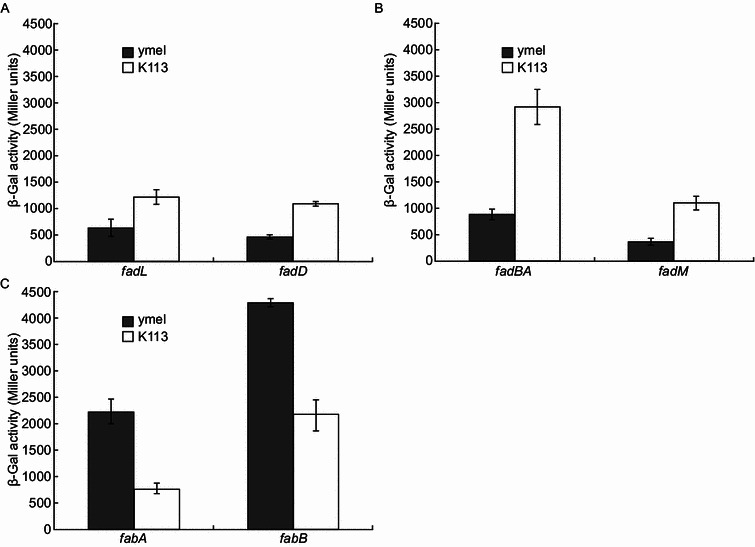
Regulatory dysfunction of fatty acid metabolism in K113fadRstrain. (A) Assays for transcriptional activities fadL and fadD, two genes of fatty acid transport system in the fadR strain K113. (B) Comparative analyses of expression levels of fadBA, a major member of beta-oxidation system and fadM, an auxiliary player of fad system in the fadR strain K113 relative to those of the wild-type ymel. (C) Effects on transcriptional levels of fabA and fabB, two key genes required for UFA synthesis due to fadR mutation in K113 strain. E. coli strains were grown in RB liquid media. β-Gal activities from three independent experiments are expressed in average ± standard deviations. In panel A, the strains used were FYJ185 (ymel, fadL-lacZ fusion), FYJ186 (K113, fadL-lacZ fusion), FYJ183 (ymel, fadD-lacZ fusion) and FYJ184 (K113, fadD-lacZ fusion). In panel B, the four strains included FYJ34 (ymel, fadBA-lacZ fusion), FYJ38 (K113, fadBA-lacZ fusion), FYJ35 (ymel, fadM-lacZ fusion) and FYJ39 (K113, fadM-lacZ fusion). In panel C, the strains tested referred to FYJ36 (ymel, fabA-lacZ fusion), FYJ 40 (K113, fabA-lacZ fusion), FYJ37 (ymel, fabB-lacZ fusion), FYJ41 (K113, fabB-lacZ fusion), respectively
