Figure 1.
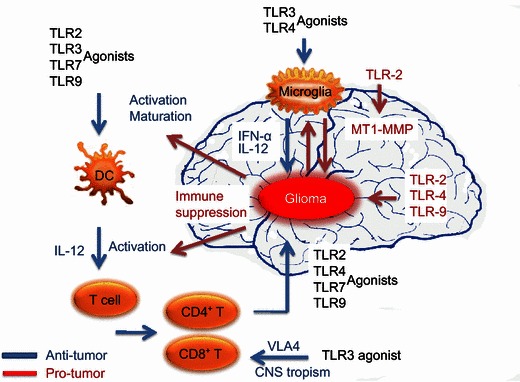
TLR agonists stimulate both anti- and pro-glioma processes. Biological activities initiated through TLR pathways are dependent on the receptor stimulated, the cell type, and the microenvironment. In the anti-glioma process, TLR agonists encourage the development of an immune environment by directly stimulating DC and T cell maturation. In addition, TLR activation in these cell types opposes the immune suppressive environment by favoring CNS tropism. Migration elevates the numbers of these cells in the CNS tumor and CLN and initiates anti-glioma immunity. TLR agonists also induce microglia isolated from primary gliomas to produce inflammatory cytokines and acquire anti-glioma activity. In contrast, activation of TLR2, TLR4, and TLR9 in microglia facilitates pro-glioma activities, such as tumor cell growth, invasion, and migration
