Figure 3.
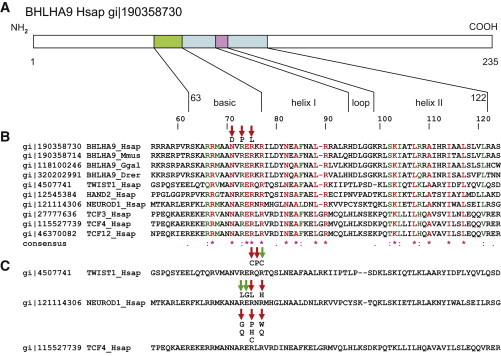
Mutations Affecting DNA Binding Sites of Human BHLHA9 and Homologous bHLH Proteins
(A) Model of human BHLHA9 with depiction of the basic helix-loop-helix region as indicated in the NCBI Protein database.
(B) Mapping of MSSD-associated missense mutations to the basic nucleic acid binding site of BHLHA9 enclosing the E-box specificity site identified with the CCD program,35 projected onto an amino acid sequence alignment of orthologous BHLHA9 sequences from various vertebrates and of human (Hsap) TCF3, TCF4, TCF12, TWIST1, HAND2, and NEUROD1 sequences generated by ClustalW.36 Numbering of amino acids refers to human (Hsap) BHLHA9. NCBI sequence identifiers (gi) are indicated. The amino acids mutated in the MSSD-affected individuals (red arrows) are conserved in all aligned proteins. Species abbreviations are as follows: Mmus, Mus musculus; Ggal, Gallus gallus; Drer, Danio rerio.
(C) Amino acid substitutions in the DNA-binding region of the basic domain of helix 1 associated with somatic mutations in cancer listed in the COSM database (green arrows) and/or clinical Mendelian phenotypes (red arrows).
TWIST1: p.Arg118Cys, in Saethre-Chotzen syndrome (SCS)23 and COSM1449859; p.Gln119Pro, SNP rs104894057, in Saethre-Chotzen syndrome;23,24 p.Arg120Cys in COSM1269548.
NEUROD1: p.Arg109Leu in COSM719047; p.Glu119Gly in COSM402132; p.Arg111Leu, rs104893649, in diabetes mellitus type II (NIDDM); p.Arg113His in COSM1217138.
TCF4: p.Arg576Gly, p.Arg576Gln, p.Arg578Pro, p.Arg578His, p.Arg580Trp, p.Arg580Gln in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome (PTHS), references in Sepp et al.;37 p.Arg578Cys in COSM563719 and COSM1141464.
The association of detrimental missense mutations affecting homologous amino acids in the basic DNA-binding region of these bHLH proteins with clinical phenotypes adds weight to the notion that the comparable mutations in BHLHA9 cause MSSD.
