Figure 3.
Segregation Analysis of the TGDS Variants and Predicted Effects on the Protein
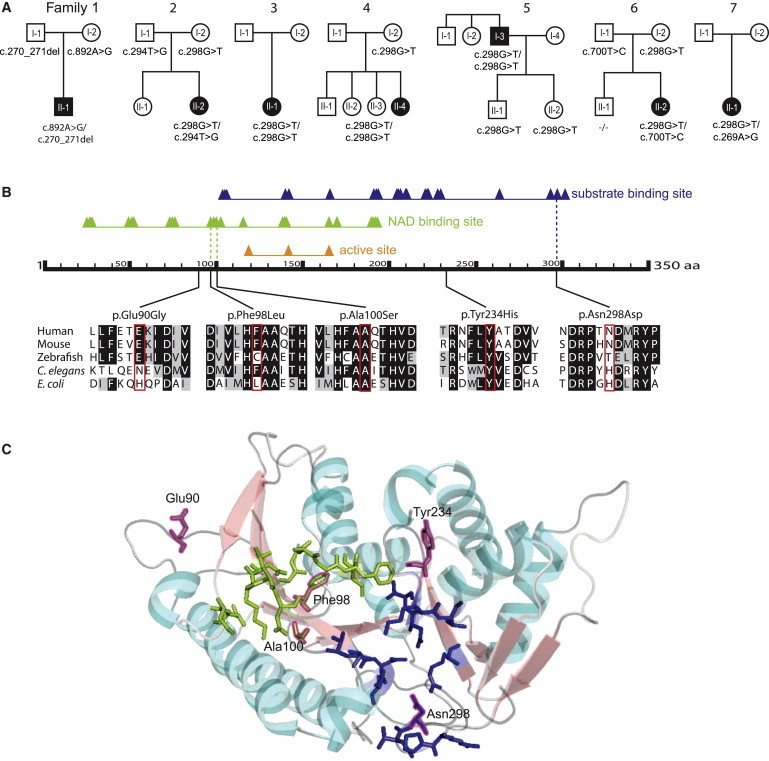
(A) Pedigree structures and TGDS genotypes for the seven families.
(B) Schematic of human TGDS showing the predicted domains, the position of the amino acid changes, and the conservation. RefSeq accession numbers are as follows: human, NM_014305.2; mouse, NP_083854; zebrafish, AAH_66615; E. coli, WP_001710460; C. elegans, NP_508390. The predicted domains are based on the Conserved Domain Database. The triangles show conserved positions. The alignment was created with BoxShade and ClustalW. The colored background of the aa in the different species indicates the degree of conservation (black, conserved; gray, similarity in properties; white, not conserved, no similarity in properties).
(C) Predicted position of the amino acid changes in the structure of TGDS in Pyrococcus horikoshii. The structure of TGDS is shown as a model created with PyMol. The substrate binding domain is shown in blue, and the NAD binding domain is in light green. The positions aligning with the amino acid changes in TGDS in our cohort are framed in magenta. Ala100 and Phe98 are localized in the NAD-binding domain, and Asn298 is in the substrate binding domain. Glu90 and Tyr234 are localized in two of the loops.
