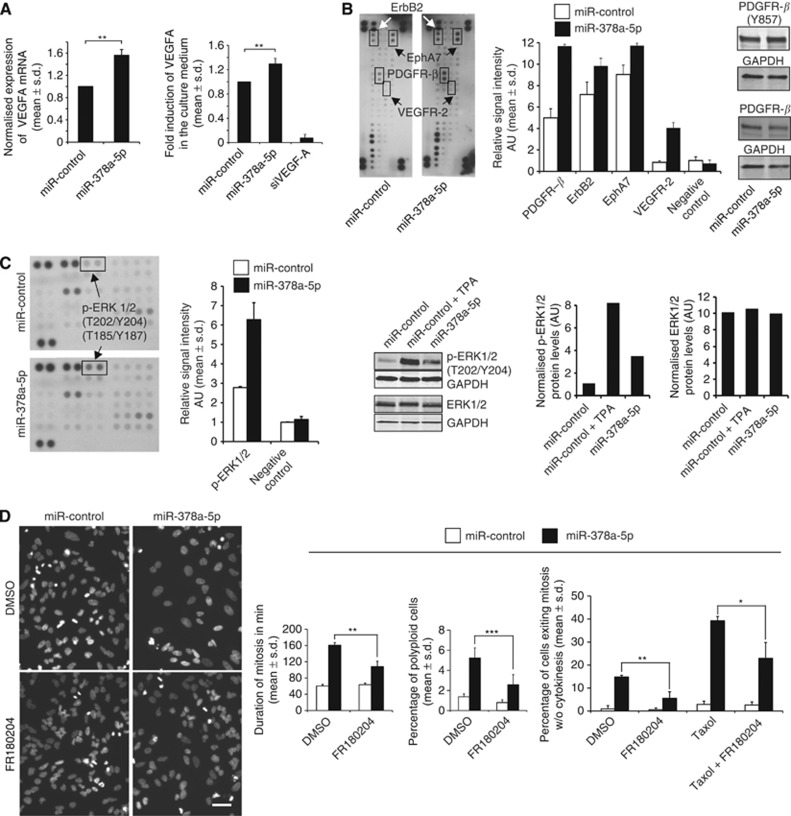
Figure 2.
Excess of miR-378a-5p increases VEGF-A production and activates the RTK–MAPK pathway. (A) The mRNA and protein levels of VEGF-A are significantly increased by miR-378a-5p in HeLa cells and in culture medium analysed at 72 h post transfection, respectively. (B) Human phospho-RTK dot blot array indicating elevated phosphorylation of PDGFR-β, ErbB2, EphRA7 and VEGFR-2 by miR-378a-5p. The graph shows quantification of the dot blot signal intensities. The results were confirmed using western blotting for phosphorylated (Y857) and non-phosphorylated PDGF-Rβ. (C) Excess miR-378a-5p increases phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (T202/Y204) without affecting total protein levels. The graphs show quantification of the phospho-kinase dot blot and pERK1/2 antibody western blotting signals. The TPA was used to stimulate ERK activation in the miR-control cells. (D) Inhibition of ERK1/2 with FR180204 partially rescues from the miR-378a-5p-induced anti-mitotic phenotype. Representative micrographs showing lowered frequency of polyploidy by miR-378a-5p upon ERK1/2 inhibition. The graphs show quantifications of mitotic duration and frequency of polyploidy and forced mitotic exit in the cell populations after indicated treatments. Data are mean±s.d. from three replicate assays (A and D). The asterisks denote statistical significances (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001). The scale bar (D)=50 μm. Abbreviation: AU=arbitrary units.