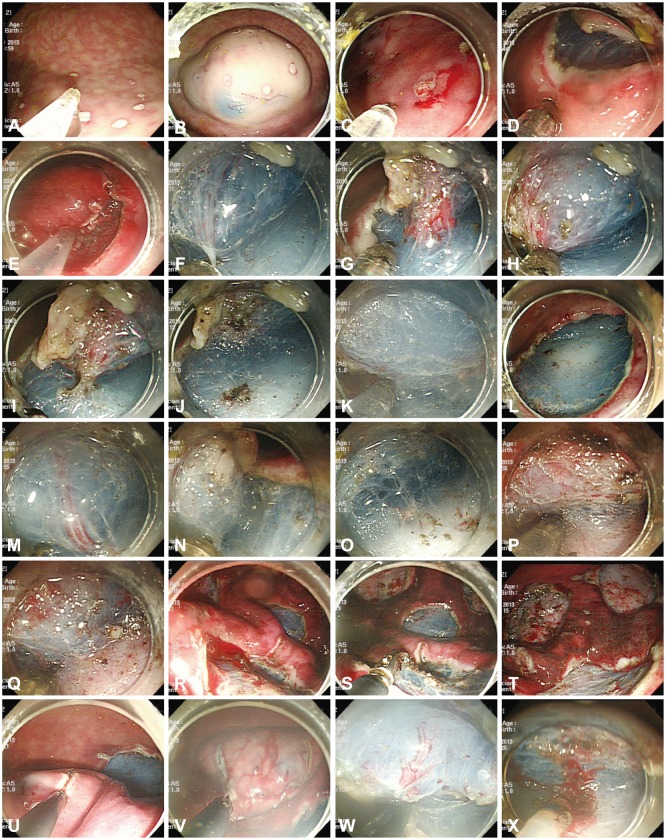
Fig. 2.
Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) procedures in the animal model. (A) Markings were made with the tip of the Optimos knife (Taewoong Medical) in the soft coagulation mode. (B) The mixed solution was repeatedly injected into the submucosal layer. (C-E) The tip of the Optimos knife was used to make the incision along the markings, using the endocut mode. (F-J) Submucosal dissection was carried out using the forced coagulation mode. The vessel was coagulated by the hooking method using the soft coagulation mode and cut using the endocut mode. (K, L) The distal remnant mucosal area was cut with the hooking method. (M-O) The knife can coagulate the small vessels of a ramified vascular network in a forced coagulation mode. (P, Q) The water injection system was used to keep enough fluid in the submucosa for continuous submucosal dissection. (R, S) The Coagrasper forceps were used to control major bleeding from large vessels, using the soft coagulation mode. (T) The post-ESD ulcers were shown to prevent bleeding afterward. (U-X) Three conventional knives (the IT-2, the Hook Knife, and the Dual knife) were used for ESD in the combination knives group.