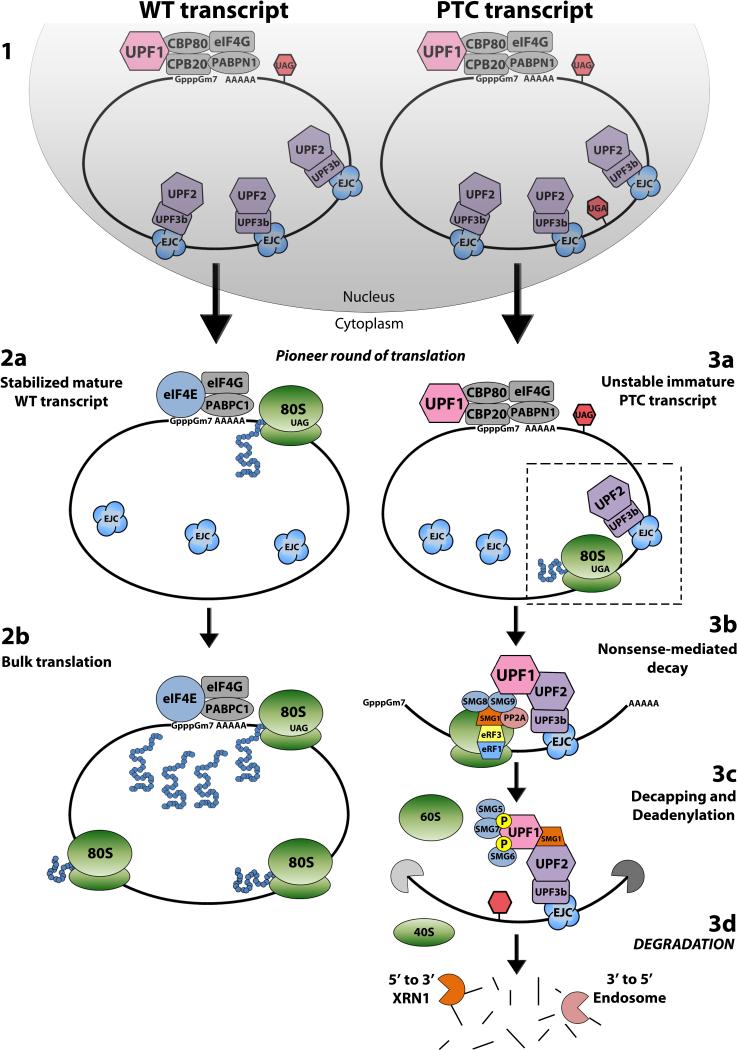
Figure 1. A Model of Nonsense-Mediated Decay.
(1) During synthesis by RNA polymerase II, wild type and PTC-bearing transcripts undergo cotranscriptional processing into messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes (mRNPs) that contain a 5’-m7GpppN cap and a poly(A)-tail. The cap-binding protein (CBP) heterodimer CBP80-CBP20 complex (CBC) binds to and protects the 5’-cap, and the nuclear poly(A)-binding protein N1 (PABPN1) and the primarily cytoplasmic PABPC1 bind to and protect the poly(A) tail along with eIF4G. In addition, the exon junction complex (EJC) is deposited 20-24 nucleotides upstream of every exon-exon splice site within the mRNP during synthesis. The CBC-bound mRNA is then exported from the nucleus(2a) Wild type transcripts are stabilized during the pioneer round of translation when the CBC is replaced by eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E), the EJCs are displaced, and PABPN1 is entirely replaced by PABPC1. The mature mRNA is then directed into (2b) steady-state rounds of bulk translation. (3a) PTC-bearing transcripts trigger the classical NMD pathway during the pioneer round of translation when the first ribosome stalls at a PTC that is located more than 50-55 nucleotides upstream of the last EJC-bearing exon-exon junction. (3b) During ribosomal stalling, eukaryotic release factor 1 (eRF1) and eRF3 bind to the ribosomal A site and associate with UPF1 which recruits SMG1 to form the SMG1-UPF1-eRF1-eRF3 (SURF) complex. SMG8 and SMG9 are then recruited to the SURF complex. (3c) The SURF complex is then translocated from the ribosome to UPF2-UPF3 on a downstream EJC. This releases SMG8 and SMG9 from SURF, allowing SMG1 to phosphorylate, and subsequently activate UPF1. Phosphorylated UPF1 triggers the dissociation of the ribosome from the mRNP and recruits SMG5, SMG6, and SMG7. This is followed by SMG5-SMG7-mediated decay of the transcript, which occurs by decapping and/or deadenylation, followed by (3d) degradation by XRN1 and the exosome complex.