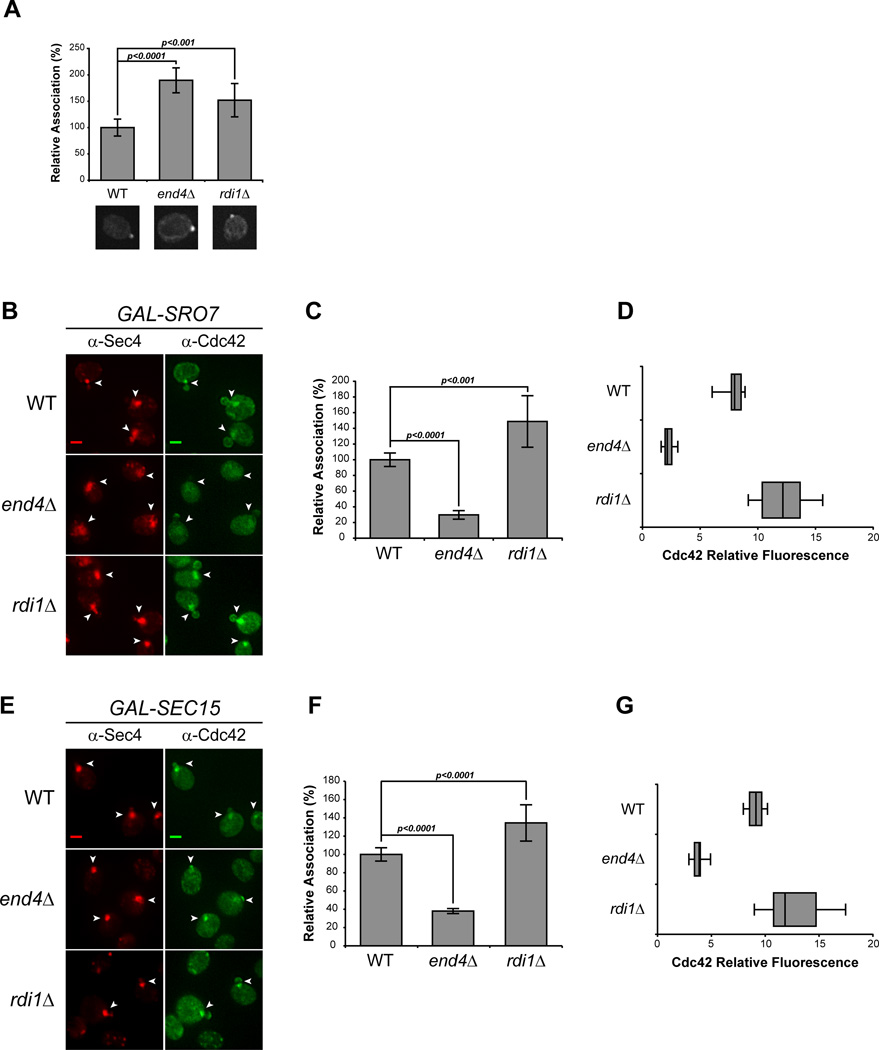
Figure 2. Endocytosis, but not Rho GDI, is required for Cdc42 association with post-Golgi vesicles.
A) Cdc42 associates with the plasma membrane polarity cap in RDI1- and END4 (SLA2)-depleted cells. Deletions in RDI1 and END4 were introduced into the GAL-SRO7 vesicle clustering strain (see Experimental Procedures). Cells were grown in raffinose media (25°C) and subjected to IF as in Figure 1. The percent association of Cdc42 at the plasma membrane polarity cap in uninduced wild-type, rdi1Δ and end4Δ cells were compared. Single-cell images represent the mean relative association; approx. 40 cells were scored; error bars represent the standard deviation. Two-tailed Student t test was performed to compare mutants to WT. B–G) Endocytic block impedes Cdc42 vesicle association. B & E) Galactose induction of vesicle clusters and IF staining was performed on wild-type, rdi1Δ, and end4Δ cells as described in Figure 1. Vesicle clusters are denoted by arrowheads. Scale bar = 2µm. C & F) Quantitative representation of the association of Cdc42 with Sro7- and Sec15-induced vesicle clusters (B & E respectively). The average Cdc42 fluorescence intensity was measured in cells randomly selected for Sec4+ vesicle clusters. Approximately 100 cells for each strain were scored. Error bars represent standard deviation. Data were normalized to percent association relative to 100% associated wild-type. Two-tailed Student t test was used to compare mutants to wild-type. D & G) Penetrance of end4Δ phenotype is shown as a box-and-whisker plot. The box represents the interquartile range (IQR) of the average relative Cdc42 fluorescence intensity. The line and whiskers denote the median and minimum/maximum, respectively.