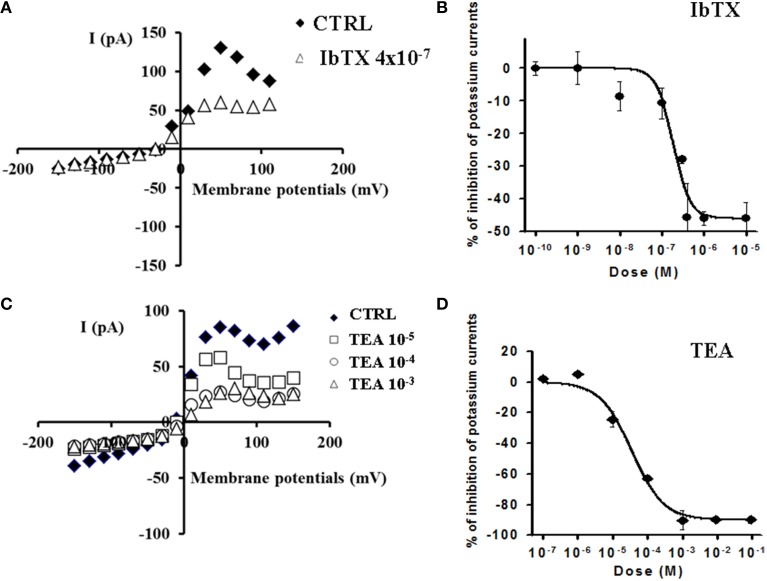
Figure 2.
Effects of the BKCa channel blockers IbTX and TEA on K+-current recorded in SH-SY5Y neuronal cell line. The effects of IbTX and TEA were investigated on the K+-current recorded in asymmetrical K+ ions concentrations (int K+: 132 × 10−3 M; ext K+: 2.8 × 10−3 M), in the presence of internal 1.6 × 10−6 M concentration of free Ca2+ ions, in the range of potentials going from −150 to +110 mV, HP = −60 mV using whole cell patch clamp technique. The whole cell K+-current was a leak subtracted and normalized to capacitance. (A) I/V relationship in the absence or presence of IbTX from a single patch. IbTX (4 × 10−7 M) reduced the outward K+-current of the −53% at +30 mV (Vm) in this patch. (B) IbTX (10−10–10−5 M) induced a concentration-dependent reduction of the K+-current at +30 mV (Vm). (C) I/V relationship in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of unselective K+ channel blocker TEA from a single patch. (D) TEA (10−5–10−3 M) induced a concentration-dependent reduction of the outward K+- current. A full reduction of the K+-current on −100% at +30 mV (Vm) was observed in the presence of TEA at 10−3 M concentration.