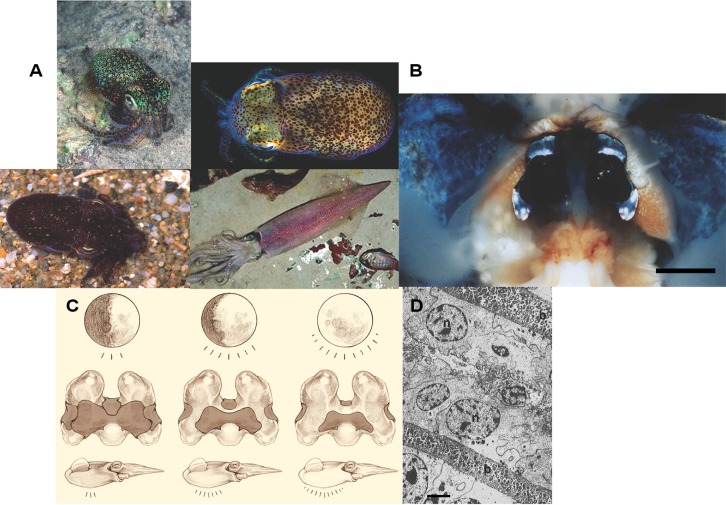
FIGURE 1.
The sepiolid squid-Vibrio symbiosis. (A) Representative species from the families Sepiolidae and Loliginidae (clockwise from upper left): Euprymna tasmanica (Sepiolidae), E. scolopes (Sepiolidae), Photololigo noctiluca (Loliginidae), and Sepiola affinis (Sepiolidae). (B) Ventral dissection of E. scolopes, showing the bilobed light organ surrounded by the ink sac. Bar = 0.5 cm. (C) Diagram how the light organ operates under different phases of the moon. The progressive decrease in shading from left to right symbolizes increased illumination by the light organ. (D) A transmission electron micrograph of an area of the epithelium-lined crypts containing symbiotic bacteria: (n) = nucleus of squid cell, (b) = bacteria in crypts (bar = 10 μm). Photo credits: Mark Norman, Mattias Oremstedt (Kahikai), M. K. Nishiguchi, R. Young, S. Nyholm, R. Long, M. Montgomery. Light organ illustration by Robert Long-Nearsight graphics.