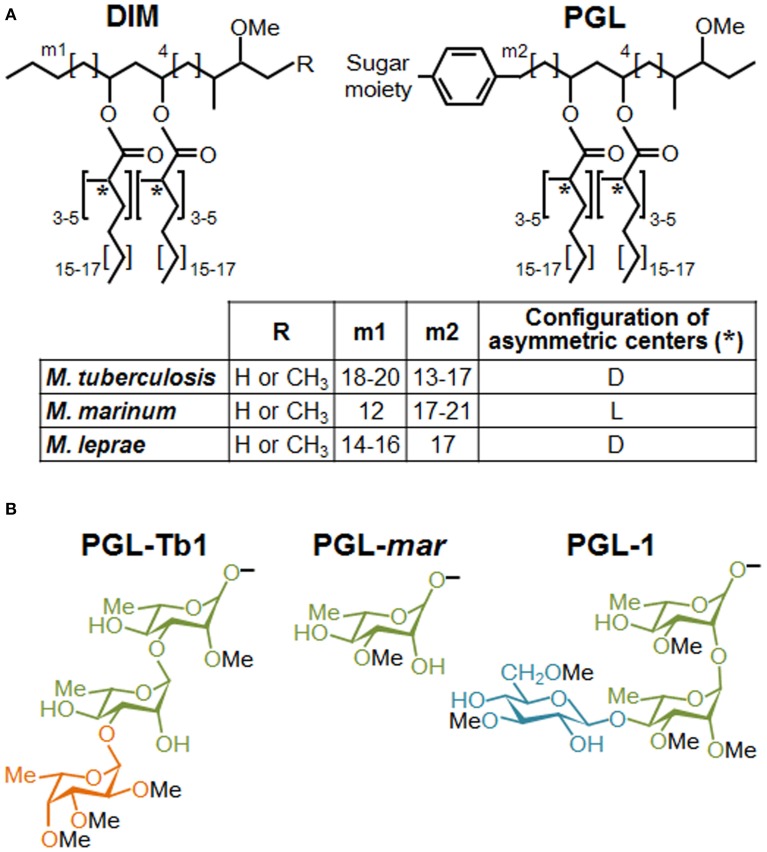
Figure 1.
Structures of DIM and PGL produced by various mycobacterial species. (A) Structure of the major DIM and PGL lipid moieties. The lipid core is composed of a long-chain β-diol (phthiocerol and phenolphthiocerol), showing slight length variations (see m1 and m2 values in embedded table), esterified by polymethyl-branched fatty acids. In most cases, the configuration of the asymmetric centers bearing the methyl branches (asterisks) are of the D series, mycocerosic acids, but in a limited number of mycobacterial species, they belong to the L series and are then called phthioceranic acids (see table). Minor structural variants of the β-diol can contain a keto group in place of the methoxy group. (B) Structure of the species-specific sugar moiety of the major forms of PGL produced by Mtb (PGL-Tb1), M. marinum (PGL-mar) and M. leprae (PGL-1). Rhamnose is represented in green, fucose in orange and glucose in blue.