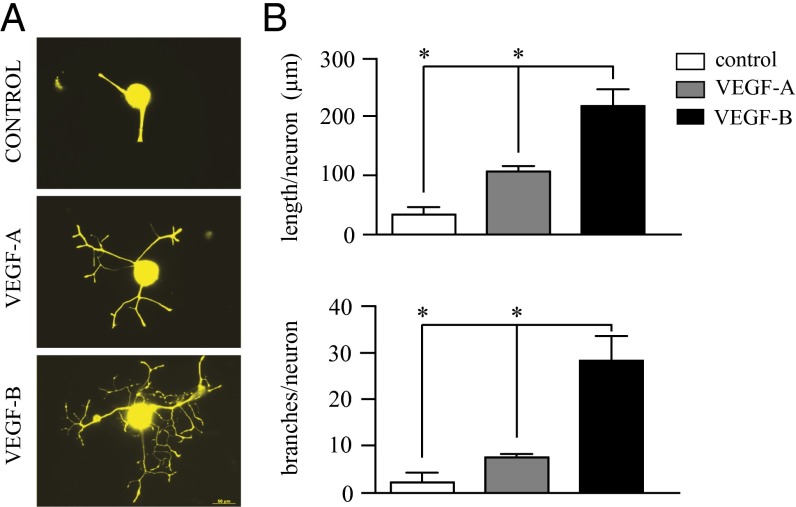
Fig. 2.
VEGF-B induces greater neurite elongation and branching than VEGF-A. Isolated trigeminal neurons were treated with either VEGF-A or VEGF-B at 50 ng/mL and neurite growth analyzed after 3 d in culture using Neurolucida software. (A) VEGF-A induced neurite growth with limited branching, whereas VEGF-B induced more extensive elongation and branching. (B) Quantification of the total neurite length demonstrated that VEGF-B induces strong growth with a greater branching area than VEGF-A. Data represent the mean ± SEM of five independent experiments. *P ≤ 0.01. (Scale bar, 50 μm.)