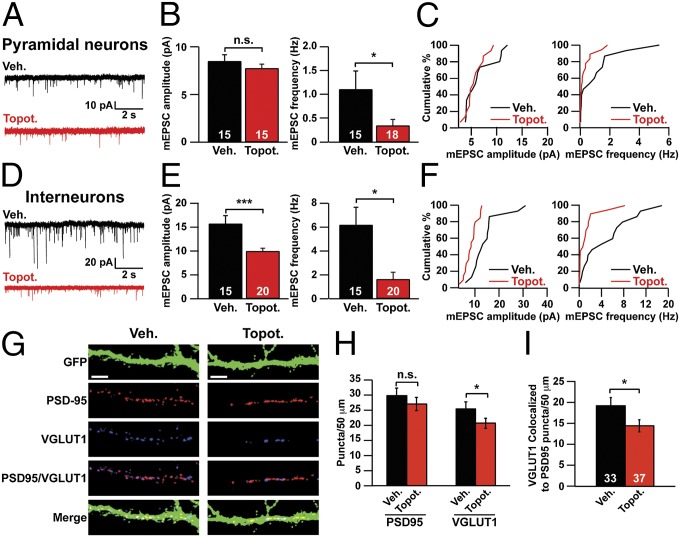
Fig. 3.
TOP1 inhibition impairs excitatory synaptic transmission and synapse formation. (A–C) Pyramidal neurons were treated with vehicle or 300 nM topotecan beginning on DIV 7 and ending on the day of recording (DIV 11–13). (A) Representative mEPSC traces. (B) mEPSC amplitude (Left) and frequency (Right). *P < 0.05 (Mann–Whitney test); n.s., not significantly different. (C) Cumulative distribution of mean mEPSC amplitudes (Left) and frequencies (Right). (D–F) Interneurons were treated with vehicle or 300 nM topotecan starting on DIV 7 and ending on the day of recording (DIV 11–13). (D) Representative mEPSC traces. (E) mEPSC amplitude (Left) and frequency (Right). ***P < 0.0005, *P < 0.05 (Mann–Whitney test). (F) Cumulative distribution of mean mEPSC amplitudes (Left) and frequencies (Right). (G–I) Cortical neuron cultures were infected with GFP lentivirus on DIV 3. Neurons then were treated with vehicle or 300 nM topotecan for 72 h, beginning on DIV 7. (G) On DIV 10, neurons were immunostained for VGLUT1 (an excitatory presynaptic marker), PSD95 (an excitatory postsynaptic marker), and GFP. (Scale bars, 10 μm.) (H) Number of PSD95 and VGLUT1 puncta per 50 μm of dendrite. n = 33 (Veh.), 37 (Topot.) neurons. *P < 0.05 (unpaired Student t test). (I) Number of colocalized VGLUT1/PSD95 puncta per 50 μm of dendrite. Data in B, E, H, and I are presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 (unpaired Student t test).