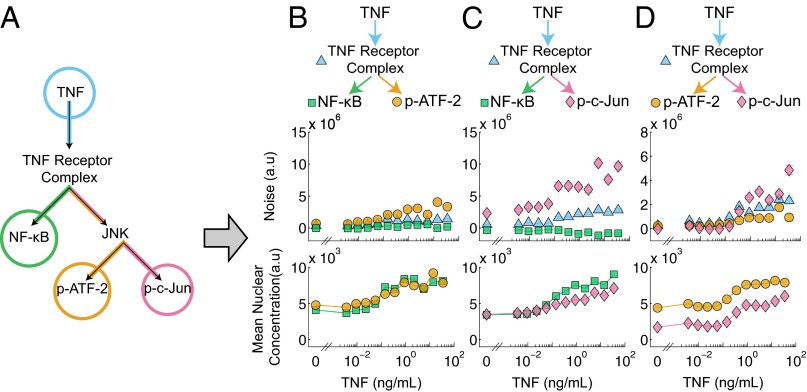
Fig. 3.
(A) Schematic illustrating the reduction of the TNF–NF-κB–JNK signaling pathway (Fig. 2A) into a six-node network which is then partitioned into three experimentally tractable four-node motifs (B–D) covering all possible transcription factor pairings. Each four-node motif consists of a TNF input, a signaling intermediary (either the TNF receptor complex or JNK), and two readouts of transcription factor activity. (B–D) The noise decomposition of the four-node motifs derived from A (Top) and the corresponding mean nuclear concentration of both transcription factors (Bottom). The JNK branch-specific noise is higher than both the NF-κB branch-specific noise and the TNF–TNFR trunk noise. Within the JNK pathway the c-Jun branch noise is greater than the ATF-2 branch noise at higher TNF concentrations. Fig. 3C is also presented as Fig. 2D.