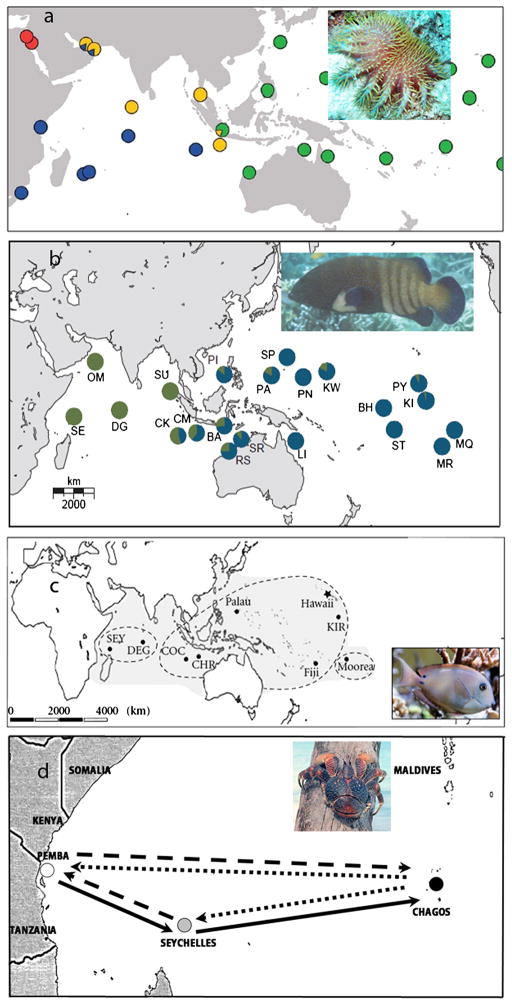
Figure 12.
(a) Crown of thorns genetic groupings. (b) peacock hind (Cephalopholis argus). (c) brown surgeonfish (Acanthurus nigrofuscus). (d) coconut crab (Birgus latro). Colour coding for the crown of thorns (Vogler et al., 2008, in prep.) and peacock hind (Gaither et al., 2011) indicate distinct genetic lineages. Dashed lines for the brown surgeonfish (Eble et al., 2011) indicate genetically independent populations. Photo credit: www.aquaportail.com. Image 12(b) and 12(c) reprinted from Gaither et al. (2011) and Eble et al. (2011) with permission from the authors. For (d) solidity of arrow lines represents relative amounts of gene flow, so that for this terrestrial crab flow is mainly eastwards during the Equatorial Counter Current flow.