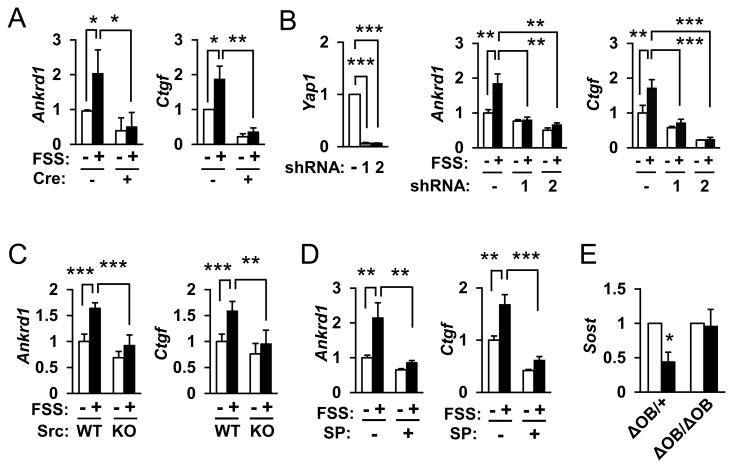
Figure 4. c-Src, JNK and YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction pathway downstream of integrin αv.
(A) Impaired expression of YAP/TAZ target genes, Ankrd1 and Ctgf, at 30 min following FSS in integrin αv-deficient osteoblasts (Cre+) by qRT-PCR. **p<0.01, *p<0.05 (n=4 each group). (B) Impaired expression of YAP/TAZ target genes in response to FSS in YAP knockdown osteoblasts. Two shRNAs against Yap1 (1 and 2) were used. - indicates scramble shRNA as negative control. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01 (n=4 each group). (C, D) Involvement of c-Src (C) and JNK (D) in the response of YAP/TAZ target genes to FSS. Primary osteoblasts from Src knockout mice (C) or wild-type osteoblasts treated with a JNK inhibitor, SP600125 (D), were subjected to FSS stimulation, and the expression of Ankrd1 and Ctgf mRNA was quantified. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01 (n=4 for B, n=6 for C, each group). (E) Attenuated response to mechanical loading in mice lacking the Itgav gene in the osteoblast lineage. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the relative abundance of Sost mRNA in the ulnae of 18-week-old female mice of the indicated genotypes subjected to mechanical loading on the right forearms (black bars), or without loading on the left forearms (white bars) as control. Data are means ± SD for six mice of each group and are expressed as a percentage of the corresponding control value. *p<0.05.