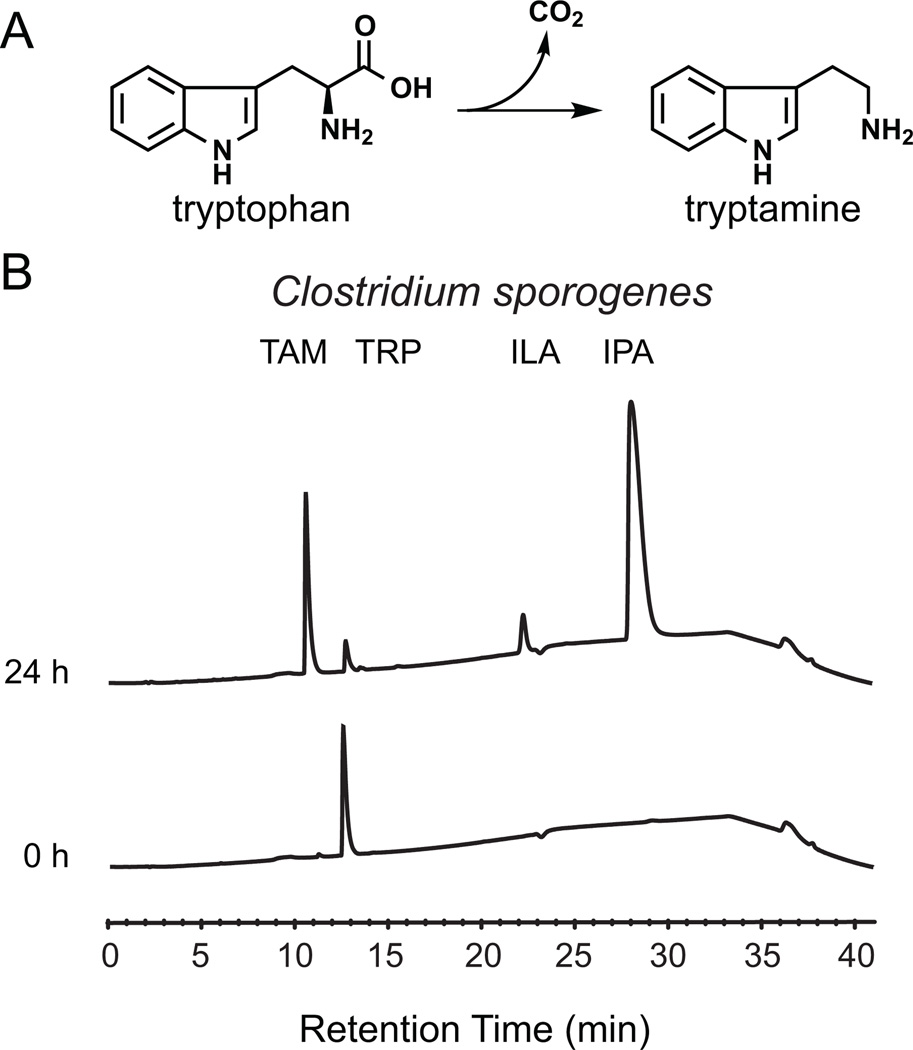
Figure 1. Tryptamine production by C. sporogenes.
(A) The proteinogenic amino acid L-tryptophan is decarboxylated to tryptamine, a biogenic amine neurotransmitter, by the action of pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent decarboxylases. (B) Whole C. sporogenes were grown anaerobically in minimal media containing 5 g/L tryptophan, and clarified supernatant was analyzed by HPLC. C. sporogenes converts tryptophan (12.5 min) into tryptamine (TAM, 10.5 min), indole lactic acid (ILA, 22 min), and indole propionic acid (28 min). See also Figure S1 and S5.