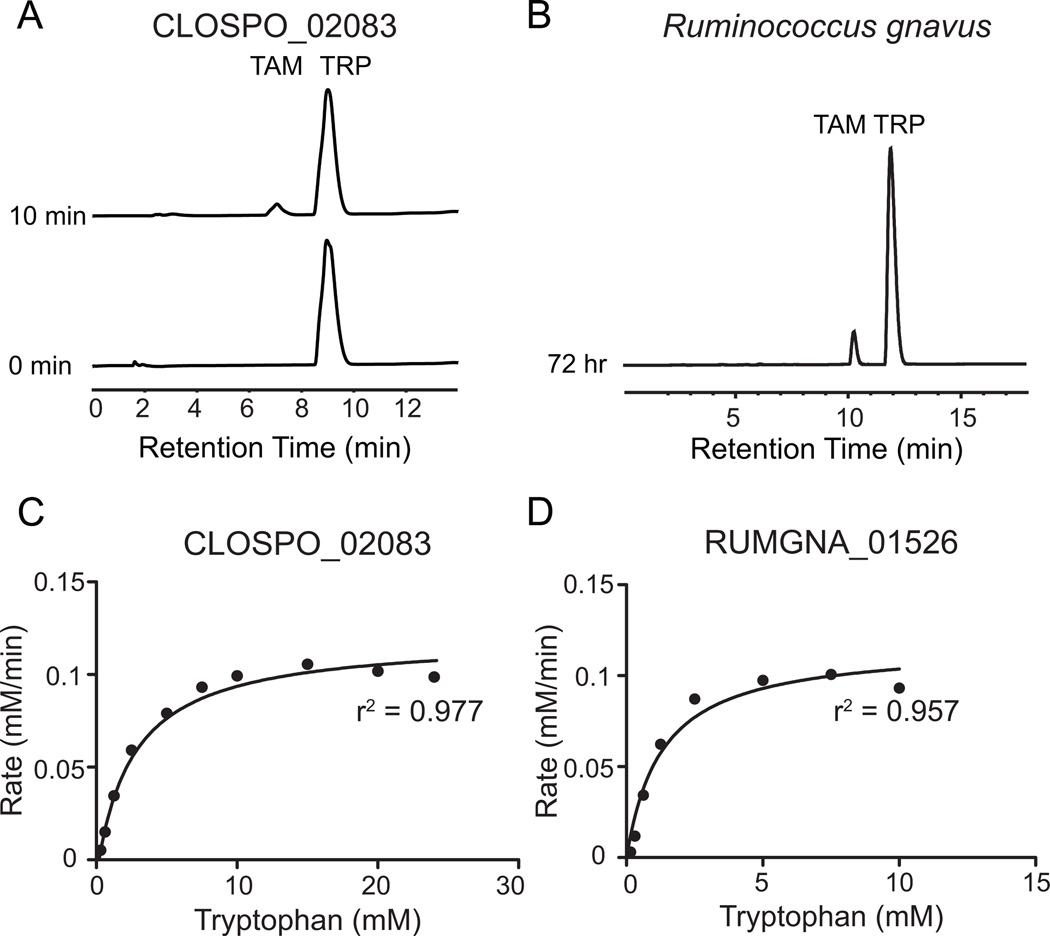
Figure 2. CLOSPO_02083 and RUMGNA_01526 are Trp decarboxylases.
(A) 100 nM purified CLOSPO_02083 was incubated with 2.5 mM tryptophan for 10 min and quenched with 1 volume MeOH; 100 µL of the reaction mixture was analyzed by HPLC. The HPLC trace shows the conversion of tryptophan (TRP, 9 min) to tryptamine (TAM, 7 min). (B) R. gnavus was grown anaerobically in minimal media containing 5 g/L tryptophan; 100 µL of the clarified supernatant was analyzed by HPLC. The HPLC trace shows the conversion of tryptophan (TRP, 12.5 min) to tryptamine (TAM, 10.9 min). Note: different HPLC methods were used for 2A and 2B. (C, D) Rate (mM tryptamine/min) vs. substrate concentration curves for tryptophan decarboxylation by (C) CLOSPO_02083 or (D) RUMGNA_01526. 100 nM enzyme was incubated with concentrations of tryptophan that varied from 0.15–24.5 mM. Error represents standard error of the mean. GraphPad was used to fit the Michaelis-Menten curve. See also Figure S2. Kinetic values are summarized in Figure S3.