Figure 2.
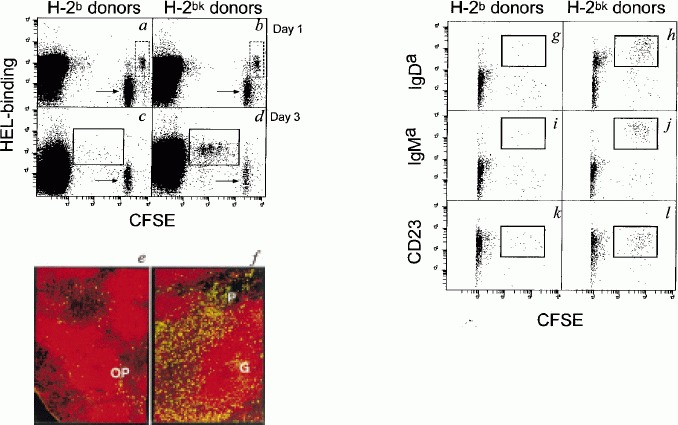
Both mature and immature Ig Tg B cells survive and proliferate when provided with T cell help upon transfer into mHEL Tg recipients. (a–d) FACS analysis of B220+ spleen cells obtained from mHEL Tg recipients of mature H-2b (a, c) or H-2bk (b, d) B cells. Undivided (dotted rectangles) and divided (solid rectangles) HEL-binding B cells are indicated. Syngeneic non-Tg B cell controls were quarter-labeled with CFSE (arrows). (e, f) Fluorescence micrographs of sections of mHEL Tg spleen 1 (e) and 5 (f) days after transfer of mature H-2bk B cells. IgMa B cells are green (FITC) and B220+ cells are red (Texas red). The outer PALS (OP), germinal centers (G) and proliferative foci (P) are indicated. (g–l) FACS analysis of B220+ spleen cells obtained from mHEL Tg recipients 3 days after transfer of immature bone marrow-derived H-2b (g, i, k) or H-2bk (h, j, l) B cells. The majority of recipient CFSE− cells were excluded from collection to increase the sensitivity of detection of CFSE+ donor-derived cells. Cells that had divided and acquired a mature phenotype are indicated (solid rectangles).
