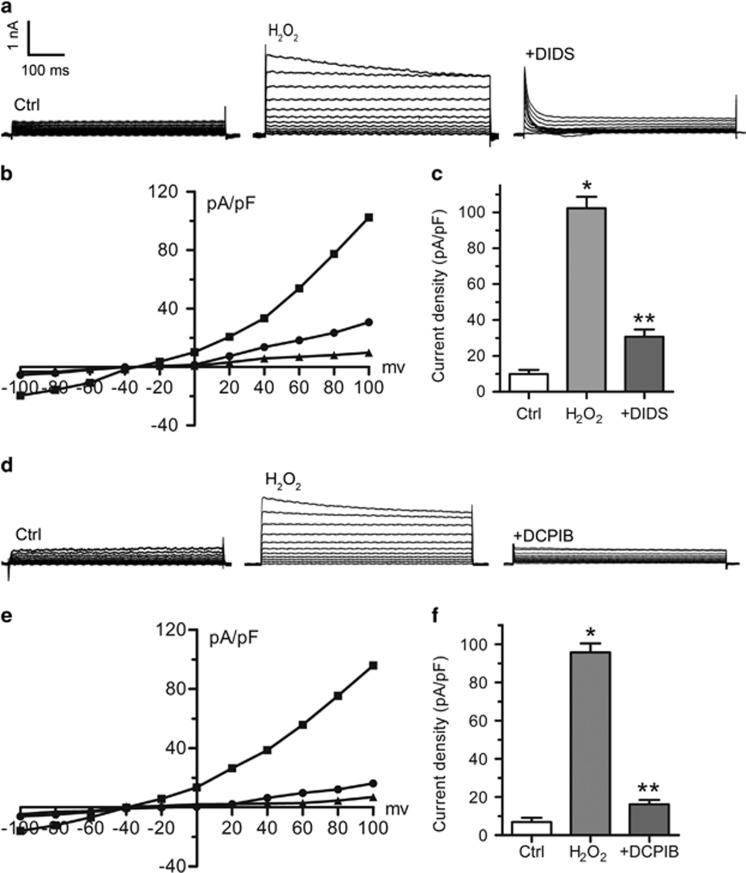
Figure 6.
ROS induce VSOR Cl− currents in cardiomyocytes. (a) Background Cl− currents recorded under isosmotic solution (Ctrl). H2O2 (500 μM)-induced Cl− currents exhibiting phenotypic properties of ICl,Vol (H2O2). H2O2-induced VSOR Cl− currents were inhibited by adding DIDS (500 μM); n=5 for each group. (b) Corresponding current-voltage (I-V) relationship for the mean current densities of isosmotic (▴), H2O2 (▪) and H2O2 with DIDS (●) conditions. (c) Current densities at +100 mV from B. *P<0.05 versus Ctrl; **P<0.05 versus H2O2, n=5. (d) Negligible background Cl− currents recorded under isosmotic solution (Ctrl). H2O2 (500 μM)-induced Cl− currents exhibiting representative properties of VSOR Cl− currents (H2O2). H2O2-induced VSOR Cl− currents were inhibited by adding DCPIB (10 μM). n=5 for each group. (e) Corresponding current-voltage (I-V) relationship for the mean current densities of Ctrl (▴), Tm (▪) and Tm with DIDS (●) conditions. (f) Current densities at +100 mV from (e). *P<0.05 versus Ctrl; **P<0.05 versus H2O2, n=5