Figure 4.
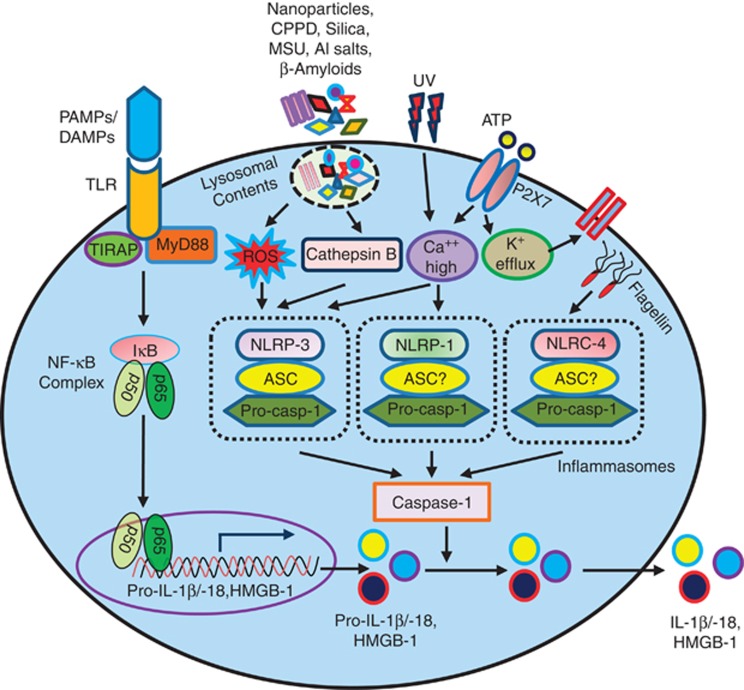
Caspase-1 activation by inflammasomes leads to pro-inflammatory cytokine production: Inflammasomes can be triggered by various stimuli. Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) through their pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) activate NLRP3 inflammasome and induce IL-1β and IL-18 secretion in the presence of ATP. In addition, external ATP, which is considered as a danger signal, causes the opening of the P2X7 receptor, leading to the release of intracellular potassium and accumulation of increased amount of Ca++. Both pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)/TLRs- and P2X7-mediated pathways work jointly to activate inflammasome complex. Besides PAMPs, the NLRP3 inflammasome can also be activated by molecules contained in the lysosomes, including crystalline and particulate substances, with the concurrent signaling driven by ATP-P2X7 axis. In presence of ATP, the crystals of uric acid and reactive oxygen species (ROS) are known to activate NLRP3 inflammasome formation, which leads to the recruitment and activation of caspase-1. IL-1β and IL-18 secretion is regulated in a two-step manner. Their transcription is induced by Toll-like receptors, which detect extracellular microbe-associated molecular patterns. After transcription, pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 are held in reserve in the cytosol unlike other cytokines and chemokines, which are secreted after production. Inflammasomes regulate a proteolytic processing step that is required for IL-1β and IL-18 to be secreted. Mature form of high mobility group box-1 (HMGB-1) is also processed and secreted through the inflammasome-mediated pathway. In addition, there are several other commonly known NLRP inflammasomes, such as NLRP1 and NLRC4, which can activate caspase-1. It has been shown that K+ efflux appears to be essential for NLRP1 activation. On the other hand, the NLRC4 inflammasome becomes activated by cytosolic flagellin. The adaptor protein apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase-recruitment domain (CARD) (ASC) is required in inflammasome complexes to bridge the interaction between upstream PRRs and inflammatory caspases through its amino-terminal pyrin domain (PYD) and carboxy-terminal CARD, respectively. However, the involvement of ASC in NLRP1 and NLRC 4 inflammasome formation is less easily understood