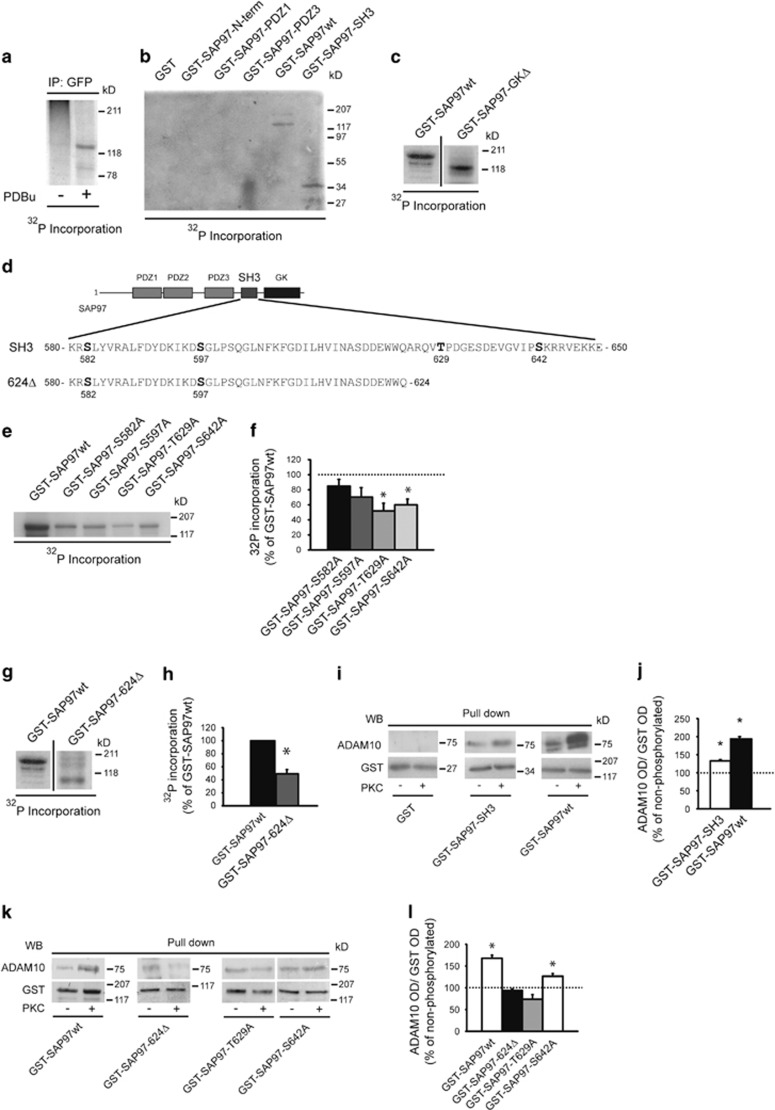
Figure 3.
PKC phosphorylation of SAP97 T629 triggers ADAM10/SAP97 association. (a) COS-7 cells transfected with YFP-SAP97wt were incubated with [32P]orthophosphate and then exposed or not to PDBu. Cell lysates were IP with anti-GFP antibody (Ab). Autoradiography revealed a specific radioactive band corresponding to YFP-SAP97 in PDBu-treated cells. (b) In vitro phosphorylation of GST-SAP97wt and GST fusion proteins of different SAP97 domains. Autoradiography revealed two specific bands corresponding to GST-SAP97wt and GST-SAP97-SH3. (c) In vitro phosphorylation of GST-SAP97wt and GST-SAP97-GKΔ. Proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and revealed by autoradiography. Samples derive from the same experiment and gel, but the lanes were non-adjacent in the gel. The lack of SAP97 HOOK-GK domains does not affect PKC phosphorylation of SAP97 (n=3, GST-SAP97-GKΔ=+0.4±7.7% P>0.05, GST-SAP97-GKΔ versus GST-SAP97wt, paired t-test). (d) SAP97-SH3 domain and SAP97-624Δ deletion mutant aa sequences. In bold is the putative PKC phosphosites. (e) In vitro phosphorylation of GST-SAP97 fusion proteins carrying single mutations of the putative PKC phosphosites. Only GST-SAP97-T629A and GST-SAP97-S642A mutants show a decrease in PKC phosphorylation compared with GST-SAP97wt. (f) Quantification of 32P incorporation of experiments in (e) (n=3, *P=0.0096 GST-SAP97-T629A versus GST-SAP97wt; P=0.0063 GST-SAP97-S642A versus GST-SAP97wt, unpaired t-test). (g) In vitro phosphorylation of GST-SAP97wt and GST-SAP97-624Δ. The lack of T629 and S642 significantly decreases PKC phosphorylation of SAP97. Samples derive from the same experiment and gel, but the lanes were non-adjacent in the gel. (h) Quantification of 32P incorporation of the experiments in (g) (n=3, *P<0.05 GST-SAP97-624Δ versus GST-SAP97wt, paired t-test). Data are expressed as the percentage of GST-SAP97wt. (i) GST-SAP97wt and GST-SAP97-SH3 were either or not in vitro phosphorylated by PKC and then incubated with rat brain HOMO to precipitate ADAM10. PKC phosphorylation increases ADAM10 binding. (j) Quantification of experiments in (I) (n=3, *P=0.01 GST-SAP97-SH3 phosphorylated versus non-phosphorylated; P=0.0026 GST-SAP97wt phosphorylated versus non-phosphorylated, paired t-test). (k) Pull-down analysis of ADAM10 binding to different mutants of GST-SAP97 after in vitro PKC phosphorylation. The lack of T629 prevents the PKC-induced increase in ADAM10/SAP97 association. (l) Quantification of experiments in (k) (n=3, *P=0.011 GST-SAP97wt phosphorylated versus non-phosphorylated; P=0.0475 GST-SAP97-S642A phosphorylated versus non-phosphorylated, paired t-test)