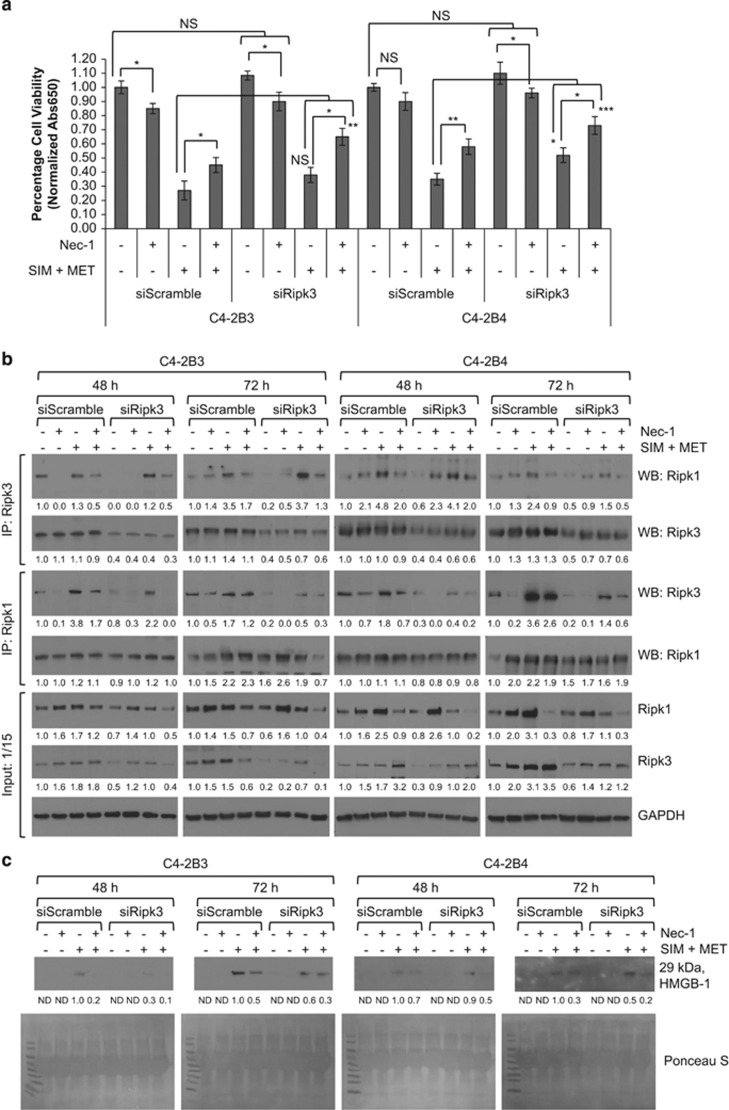
Figure 8.
SIM+MET-induced necrosis in C4-2B metastatic CRPC cells is both Ripk1- and Ripk3 dependent. (a) Percentage cell viability (mean±S.D.) by the methylene blue assay in non-targeting (siScramble) and Ripk3-targeting (siRipk3) siRNA transfected C4-2B3 and C4-2B4 cells following treatment with 50 μM Ripk1 inhibitor necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) or combination 4 μM simvastatin (SIM) and 2 mM metformin (MET)±25−100 μM Nec-1 for 72 h, n=3 separate experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, NS=not significant, as determined by ANOVA followed by the Tukey multiple comparison procedure. (b) Treatment of C4-2B3 and C4-2B4 cells with 50 μM Nec-1 for 72 h and siRNA knockdown of Ripk3 expression additively reduces Ripk1–Ripk3 association. Immunoprecipitation of 600 μg protein from total cell lysates of non-targeting (siScramble) and Ripk3-targeting (siRipk3) siRNA-transfected C4-2B3 and C4-2B4 cells treated with 50 μM Nec-1 and/or combination 4 μM SIM and 2 mM MET was conducted with Ripk1 and Ripk3 antibodies followed by western blot with Ripk1, Ripk3, and GAPDH antibodies. No GAPDH was detected in immunoprecipitates (not shown). Forty μg protein from total cell lysates were also immunoblotted as a control (input). Protein expression was quantified by densitometry normalized to GAPDH loading control (mean from two separate experiments). Ripk3 siRNA resulted in 62−64% knockdown in Ripk3 protein expression at 48 h and 48−56% knockdown at 72 h. (c) Western blot analysis of HMGB-1 protein in 40 μl conditioned media from non-targeting (siScramble) and Ripk3-targeting (siRipk3) siRNA-transfected C4-2B3 and C4-2B4 cells following treatment with 50 μM Nec-1 and/or combination 4 μM SIM and 2 mM MET for 48−72 h. HMGB-1 protein expression quantified by densitometry (mean from two separate experiments). ND, none detected. Ponceau S stain used to demonstrate equal loading