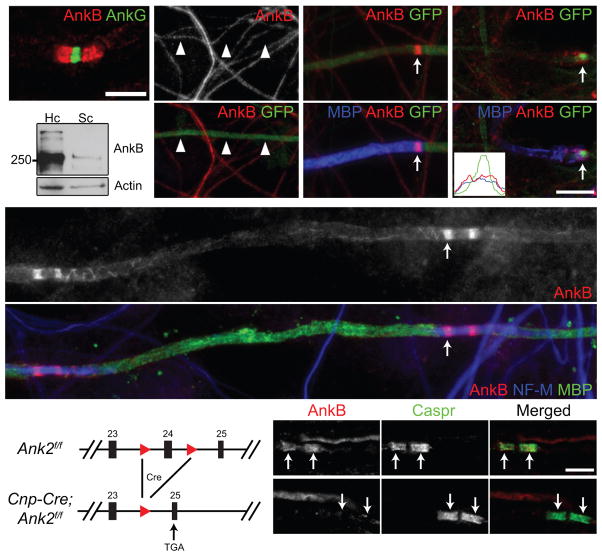
Figure 1.
Paranodal AnkB is derived from Schwann cells in the PNS. (a) Immunostaining of a mouse sciatic nerve for AnkG (node, rabbit polyclonal anti-AnkG) and AnkB (paranodes, N105/17). (b) Cultured DRG neurons were infected with adenovirus carrying a GFP and AnkB shRNA-expressing construct, and immunostained (AnkB, N105/13). Arrowheads point to the GFP-positive axon. (c, d) Schwann cells were added to the same culture as in (b) and induced to myelinate. The co-culture was labeled for myelin basic protein (MBP), GFP and AnkB (N105/13 (c) or N105/17 (d)). The arrows point to paranodal AnkB. A line scan of fluorescence intensity of the paranode indicated in (d) is shown in the inset. (e) Immunoblots of lysates from rat hippocampal (Hc) neuron and purified Schwann cell (Sc) cultures (AnkB, N105/17). The full blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 3. (f) DRG neurons from the AnkB conventional KO were co-cultured with myelinating rat Schwann cells and immunostained for AnkB (N105/17), neurofilament-M (NF-M) and MBP. The arrow points to a paranode. Localization of AnkB along the inner mesaxon13 was also observed as spiral extensions from paranodal junctions. (g) The scheme of the Ank2 conditional allele. The two loxP sites (red triangles) flank exon 24. After Cre recombination and removal of exon 24, a premature stop codon is generated in exon 25. (h, i) Immunostaining of 4-week-old AnkB-cHet (h) and AnkB-cKO (i) sciatic nerves (AnkB, rabbit polyclonal anti-AnkB). Arrows point to paranodal junctions. Scale bars = 5 μm (a; h, i), and 10 μm (b–d, f).