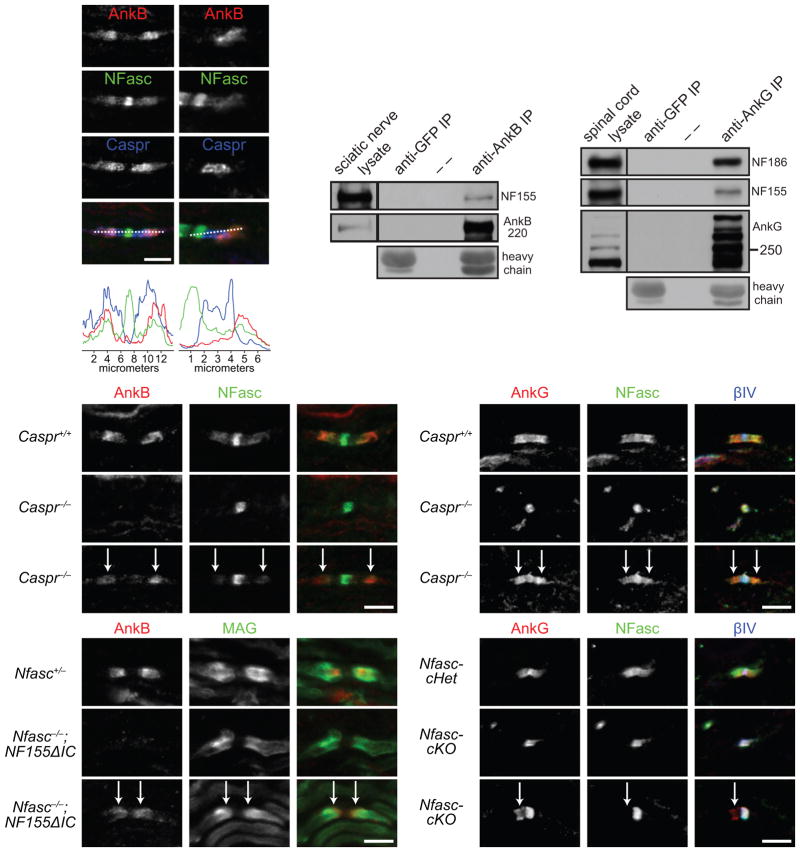
Figure 6.
AnkB and AnkG interact with NF155 in vivo and can be targeted to paranodes independently of paranodal junctions and NF155. (a–d) P8 sciatic nerve sections were stained for AnkB (N105/17), NFasc and Caspr (a, b), and the respective longitudinal line scans are shown (c, d). (e) Immunoprecipitation of AnkB from adult rat sciatic nerves co-precipitated NF155. Immunoprecipitation with the anti-GFP antibody served as a negative control. Heavy chain, mouse IgG heavy chain. AnkB was detected by H-300 rabbit polyclonal antibodies. (f) Immunoprecipitation of AnkG from P21 mouse spinal cords co-precipitated NF186 and NF155. AnkG was detected by the goat polyclonal antibodies. The immunoprecipitation in (e, f) was reproduced at least three times. The full blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 3. (g–i) Immunostaining of P7 sciatic nerves (AnkB, rabbit polyclonal). Arrows point to the residual AnkB and NFasc at paranodes. (j–l) Immunostaining of P7 spinal cords (AnkG, N106/36). Arrows point to the residual AnkG and NFasc at paranodes. (m–o) Immunostaining of P5 sciatic nerves (AnkB, rabbit polyclonal). Arrows point to the paranodes with residual AnkB. (p–r) Immunostaining of P12 Nfasc-cHet (Cnp-Cre;Nfascf/+) and Nfasc-cKO (Cnp-Cre;Nfascf/f) spinal cords (AnkG, N106/36). Two mice per genotype and more than 100 nodes were examined in each mouse. 80–190 nodes per animal were quantified. Scale bars = (a, b) 5 μm for (a) and 3.3 μm for (b); 5 μm (g–i, j–l, m–o, and p–r).