Fig. 4.
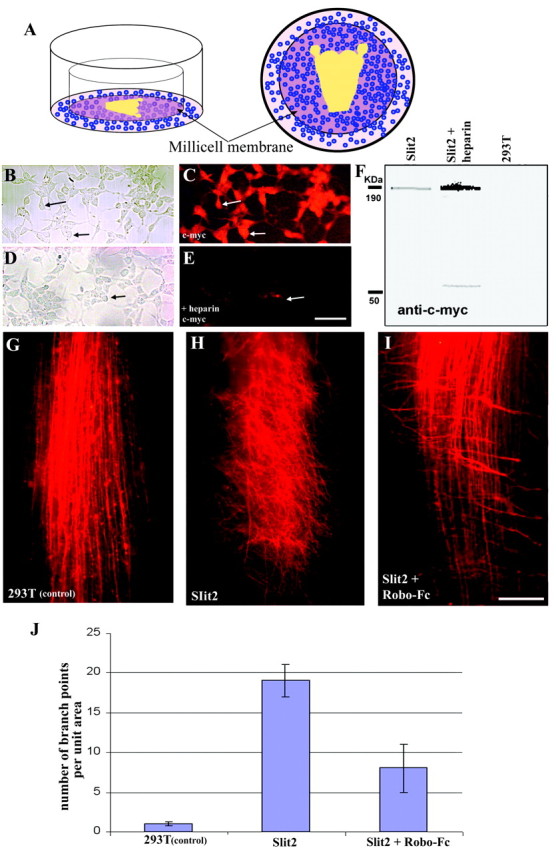
Effect of Slit2 on central trigeminal tract axons.A, Diagram of the culture setup. Explants are schematized within the center of the well; blue circlesdepict HEK293Tcells, which are just below and around the membrane with the whole-mount preparation. B, HEK293T cells transfected with hSlit2. C, c-Myc immunohistochemistry of cells shown in B (arrows in both micrographs point to the same cells). D, HEK293T cells transfected with hSlit2. E, c-Myc immunohistochemistry of cells shown in D after heparin treatment (arrow points to the same cell group in both micrographs). F, Western blot of the medium from hSlit-2-transfected cells and untransfected (control) cells.G, Low-magnification view of DiI-labeled trigeminal tract axons in a brainstem–TG intact whole-mount preparation grown in the presence of untransfected HEK293T cells (control).H, DiI-labeled trigeminal tract axons in a brainstem–TG intact whole-mount preparation grown in the presence of HEK293T cells transfected with hSlit2. I, DiI-labeled trigeminal tract axons in a brainstem–TG intact whole-mount preparation grown in the presence of HEK293T cells transfected with hSlit2 and Robo-Fc conditioned medium.J, Bar graph representation of the number of branch points per unit area for each case (see Materials and Methods). In the presence of Slit2, the number of branch points per unit area shows a highly significant increase (p < 0.0005). Addition of Robo-Fc conditioned medium causes a statistically significant reduction (p < 0.001) in the number of branch points per unit area. Error bars represent one SD. Scale bars: B–E, 30 μm; G–I, 100 μm.
