Figure 4.
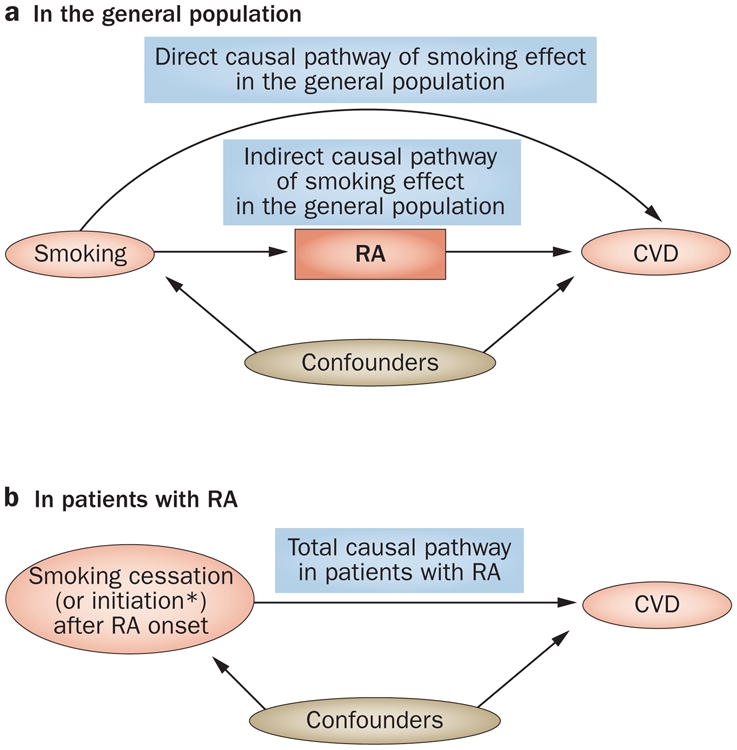
Causal diagrams displaying the effect of smoking on CVD a | A causal diagram displaying two causal pathways (direct and indirect) for the total effect of smoking on CVD complications in the general (unselected) population. The box around ‘confounders’ denotes adjustments. The total effect of smoking on the risk of CvD in this population is the net combined causal effect through both pathways. b | A causal diagram of the total causal effect of smoking on CVD complications among patients with RA (i.e. a restricted population). *Theoretically, smoking initiation after RA onset would be equivalent to smoking exposure in the general population in part a; however, in practice, this would be unusual after RA onset. Alternatively, the impact of smoking cessation can be evaluated in these studies. Abbreviations: CVD, cardiovascular disease; RA, rheumatoid arthritis.
