Figure 5.
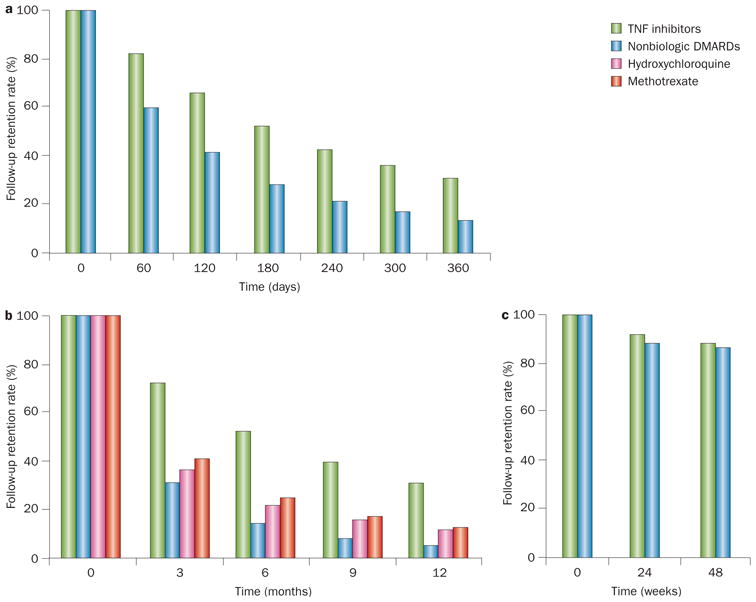
Differential loss to follow-up in studies of RA therapy. a,b | Two observational pharmaco-epidemiological studies46,47 showed high and differential loss rates between groups. c | By contrast, much lower levels of loss to follow-up were observed in a randomized trial46 of a biologic agent in RA at similar time points. Despite effectively controlling for confounders in the observational studies,46,47 such a high level of differential loss to follow-up threatens the embedded assumption that loss to follow-up is completely random (i.e. not associated with an outcome, or mediators of an outcome), leaving the study design open to potential selection bias. Abbreviation: RA, rheumatoid arthritis.
