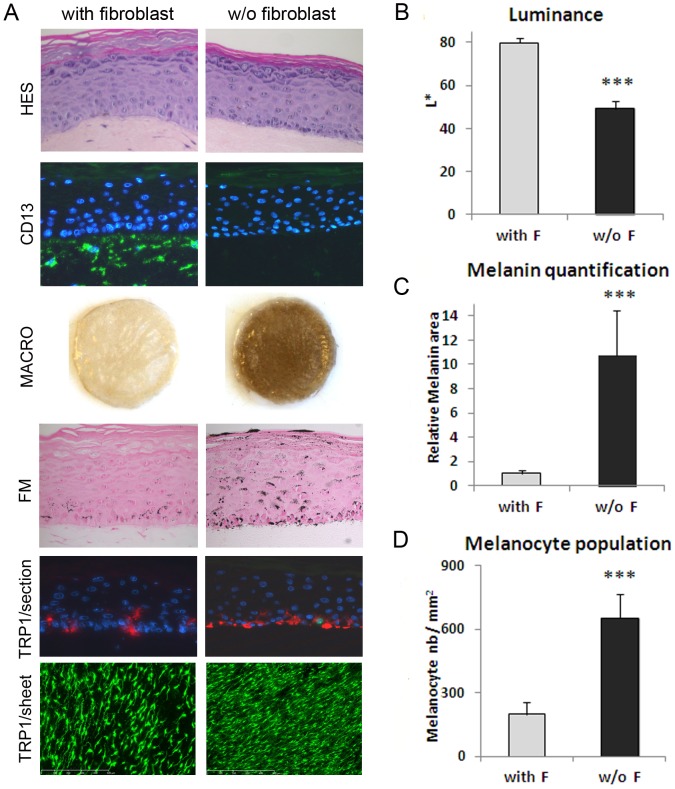
Figure 1. Microscopic examination and measurement of pigmentation in the in vitro pigmented skin model reconstructed in the presence or absence of fibroblasts in the dermal compartment.
A) Microscopic examination of HES staining of cross-sections showed a correct epidermal architecture and differentiation process leading to the development of a stratum granulosum and stratum corneum in both 3D systems. The CD13 staining (green) of cross-sections confirmed the presence or absence of fibroblasts (from adult 21 yr-old donor) in the dermal equivalent. Macroscopic pictures of PRS illustrate the resulting drastic difference in pigmentation between the two conditions which was confirmed by B) Luminance measurement (mean of 3 experiments). Fontana-Masson staining for melanin granules detection (black points), and C) graph of melanin quantification (mean of 3 experiments) performed by image analysis of Fontana-Masson (FM) staining on cross-sections. To compare the two conditions, results on melanin content were normalized to the control condition (with fibroblasts). TRP-1 staining (red) of cross-sections shows melanocytes positioned at the basal layer of the epidermis in both 3D systems. TRP-1 staining (green) of PRS epidermal sheets and D) corresponding graph of melanocyte quantification (mean of 3 experiments) performed by image analysis. The values represent means ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance was evaluated by the Student's t-test; *** p-value <0.001. Magnification: A HES, FM = x400, CD13, TRP1/section = x200, TRP1/sheet = x50.