Fig. 4.
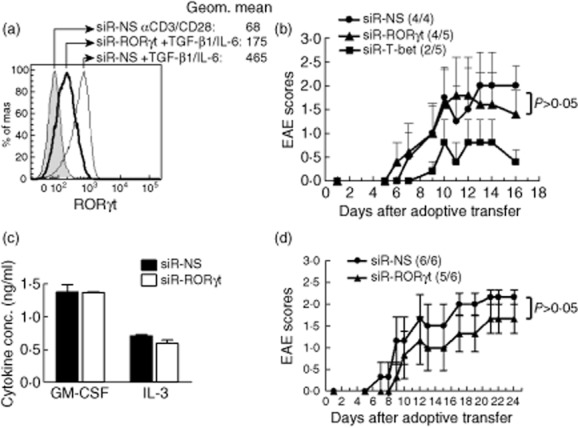
Suppressing retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt) expression does not significantly reduce T cell encephalitogenicity. (a) Splenocytes from naive B6 mice were transfected with either siRNA-NS or siRNA-RORγt for 18 h. The cells were then activated with αCD3/CD28 alone or in the presence of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 and interleukin (IL)-6 for 2 days. RORγt expression was determined by intracellular staining (filled grey histogram represents siRNA-NS treated cells activated with αCD3/CD28; thin-line open histogram represents siRNA-NS treated cells activated with αCD3/CD28 plus TGF-β1 and IL-6; bold-line open histogram represents siRNA-RORγt-treated cells activated with αCD3/CD28 and TGF-β1 and IL-6). Cells were gated on CD4+ T cells. (b) Splenocytes from naive TCR Vα2·3/Vβ8·2 transgenic mice were transfected with siRNA-NS, siRNA-RORγt or siRNA-T-bet for 18 h. The cells were then activated with myelin basic protein (MBP) Ac1-11 for 3 days and transferred into naive B10 PL recipient mice by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection. The mice were monitored for experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) development. (c,d) Splenocytes from naive IFN-γ–/– TCR Vα2·3/Vβ8·2 transgenic mice were transfected with siRNA-NS or siRNA-RORγt for 18 h. The cells were then activated with MBP Ac1-11 for 3 days and transferred into naive B10 PL recipient mice by i.p. injection. Supernatant was collected 72 h after activation and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and IL-3 production were analysed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (c). The recipient mice were monitored for EAE development (d). Data are representative of two independent experiments.
