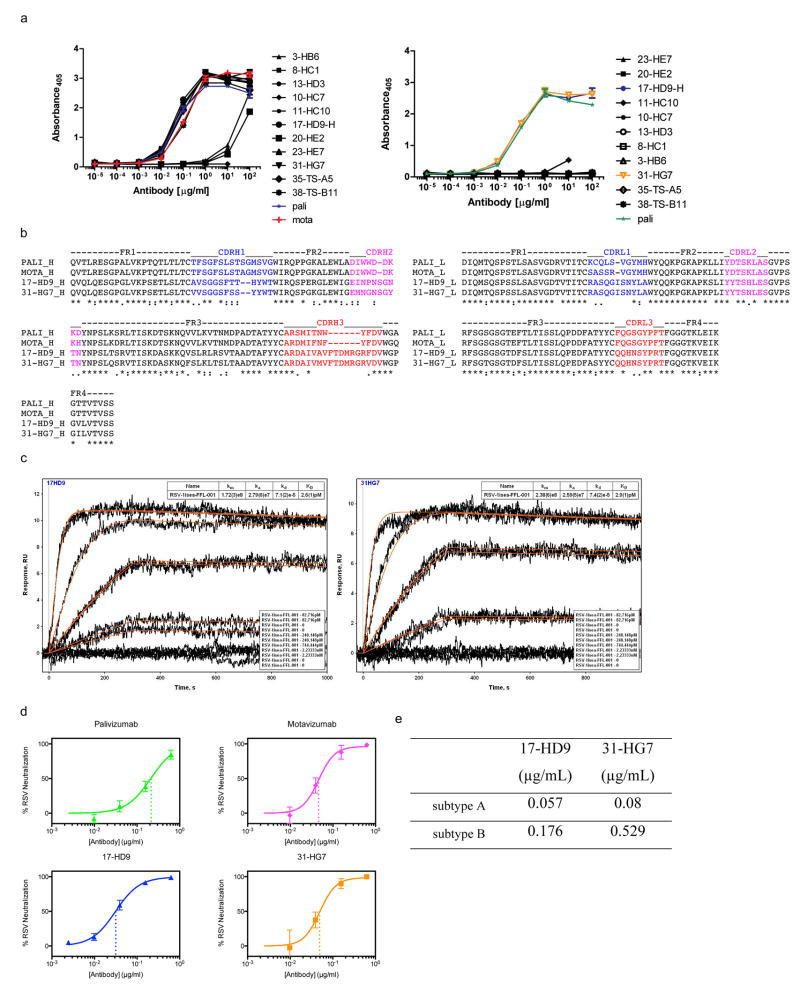
Extended Data Figure 8.
Properties of NHP mAbs isolated by B cell sorting from an animal immunized with HBcAg-FFL_001. a) ELISA binding of recombinant NHP mAbs to FFL_001 (left) and recombinant RSV F glycoprotein (right). b) Sequence alignment of heavy (left) and light (right) chains of the Fv domains of NHP mAbs 17-HD9 and 31-HG7 along with Mota and Pali. c) SPR data for mAbs 17-HD9 and 31HG7 binding to FFL_001. mAb IgGs were captured by anti-human IgG on the sensor chip (mAbs were expressed with human Fc) and FFL_001 was flowed as analyte. d) Head-to-head comparison of the neutralization potency of NHP mAbs, Mota, and Pali in the plaque reduction assay. The data values are shown as mean ± standard deviation from two assays. The data were fit by the equation for one site specific binding with Hill slope, implemented in GraphpadPrism. According to the fits, the IC50s were 0.21 ug/mL (Pali), 0.046 ug/mL (Mota), 0.031 ug/mL (17-HD9), and 0.049 ug/mL (31-HG7). e) EC50 values for neutralization of RSV subtypes A and B by 17-HD9 and 31-HG7 as reported by the flow cytometry assay.