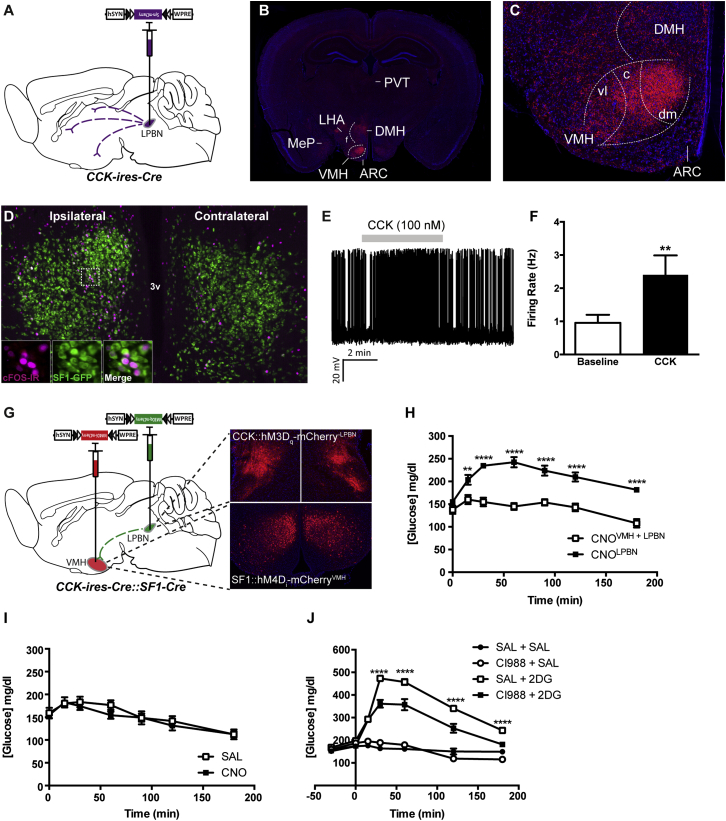
Figure 4.
CCKLPBN Neurons Engage SF1VMH Neurons to Mediate CR-Responses
(A) Unilateral stereotaxic injection of Cre-dependent synpatophysin-mCherry virus into the LPBN of CCK-ires-Cre mice facilitated genetically defined tract tracing of CCKLPBN neuron projections.
(B and C) CCKLPBN neurons send ascending projections to the ipsilateral hypothalamus, including the lateral hypothalamus (LH), dorsomedial nucleus (DMH), and VMH.
(D) CNO-mediated activation of unilateral CCK-ires-Cre::hM3Dq-mCherryLPBN neurons evokes cFOS-IR (magenta) within ipsilateral SF1VMH neurons (green) in CCK-ires-Cre::SF1-Cre::R26-loxSTOPlox-L10-GFP mice.
(E and F) A total of 55% (5/9) of synaptically isolated SF1VMH neurons were activated by CCK (CCK-8S, 100 nM) in ex vivo slice preparations maintained under hypoglycemic conditions (0.5 mM glucose).
(E) Representative electrophysiological trace of a SF1VMH neuron demonstrating CCK-induced activation.
(F) CCK-responsive SF1VMH neurons exhibited a 2.5-fold increase in firing frequency over baseline upon CCK-8S administration (n = 6, paired t test, t(4) = 4.1, p = 0.01).
(G and H) Functional occlusion of CCKLPBN neuron glucoregulation through concomitant silencing of downstream SF1VMH neurons.
(H) SF1-Cre::hM4Di-mCherryVMH silencing prevents the CCK-ires-Cre::hM3Dq-mCherryLPBN-mediated CR-response in CNO-treated double transduced mice, as compared to CCK-ires-Cre::hM3Dq-mCherryLPBN only transduced mice (n = 5 per group; two way ANOVA, main effect of treatment [F(1,56) = 188.2, p < 0.0001], main effect of time [F(6,56) = 11.9, p < 0.0001], and interaction [F(6,56) = 4.5, p = 0.0009]; Sidak’s post hoc test for individual time point analysis).
(I) SF1VMH neuron silencing does not influence blood glucose concentrations compared to saline (n = 4; repeated-measures ANOVA; main effects of treatment, time, and interaction not significant).
(J) The CR-response to 2DG was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with the selective CCKB-receptor antagonist CI988 (n = 5 per group; two-way ANOVA; main effect of treatment [F(3,112) = 369.1, p < 0.0001], main effect of time [F(6,112) = 121.7, p < 0.0001], and interaction [F(18,112) = 36.2, p < 0.001]; post hoc comparisons determined by Tukey’s post hoc test for individual time point analysis).
Abbreviations: ARC, arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus; DMH, dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; MeP, medial amygdaloid nucleus posterior part; PVT, paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus; SAL, saline; VMH, ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus; c, central; vl, ventrolateral; dm, dorsomedial. All data are presented as mean ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.