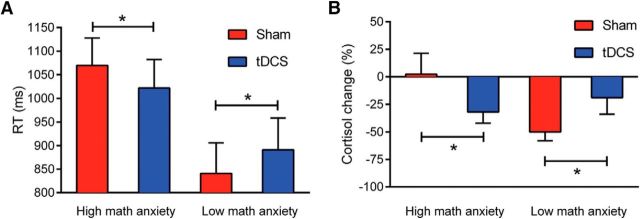
Figure 1.
Mathematics anxiety-dependent effects of tDCS. A, Behavioral double dissociation between high and low mathematics anxiety groups. For the high mathematics anxiety group (n = 25), tDCS produced faster arithmetic decisions compared with sham stimulation. For the low mathematics anxiety group (n = 20), tDCS impaired arithmetic decision RTs compared with sham (both ps < 0.001). B, Double dissociation in salivary cortisol concentration between high and low mathematics anxiety. Negative cortisol change indicates lower cortisol concentrations at post-test compared with pre-test. High mathematics anxiety participants showed greater cortisol reductions after real stimulation, while low mathematics anxiety participants showed greater cortisol reductions after sham stimulation (both ps < 0.05). *p < 0.05. Error bars represent 1SEM.