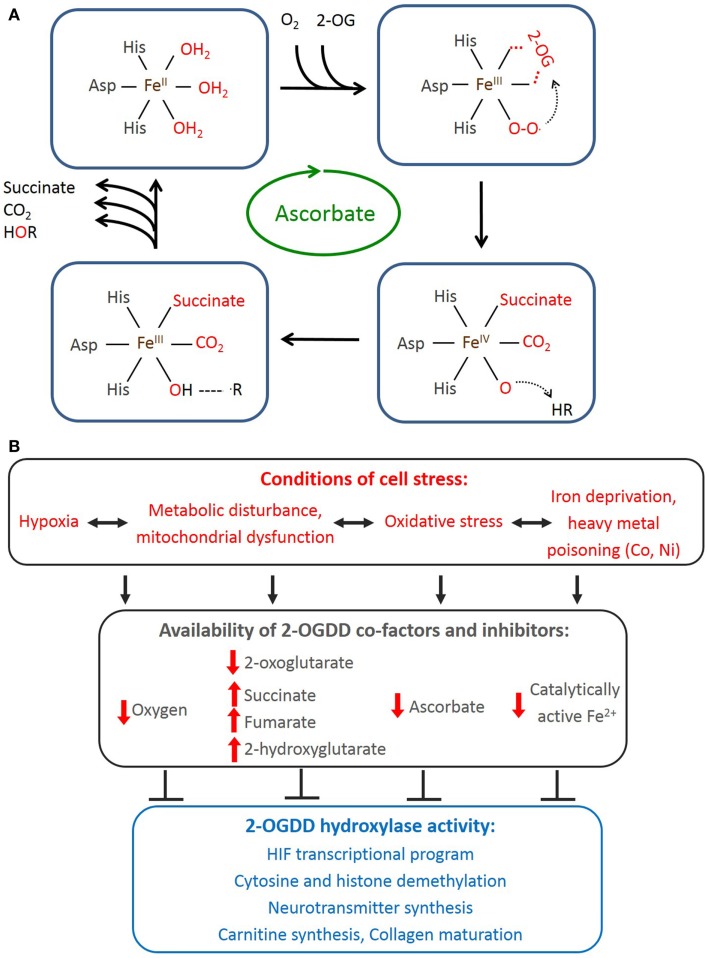
Figure 1.
2-Oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase reaction cycle and factors affecting their activity in mammalian cells. (A) Representation of 2-OGDD catalytic cycle. One atom of molecular oxygen is incorporated into the hydroxylated substrate and the other into succinate. 2-OG is converted to succinate, releasing CO2. Ferrous iron and ascorbate are specific co-factors for this reaction. (B) Cellular stressors deprive 2-OGDDs of their required co-factors resulting in inhibition of multiple potential pathways.