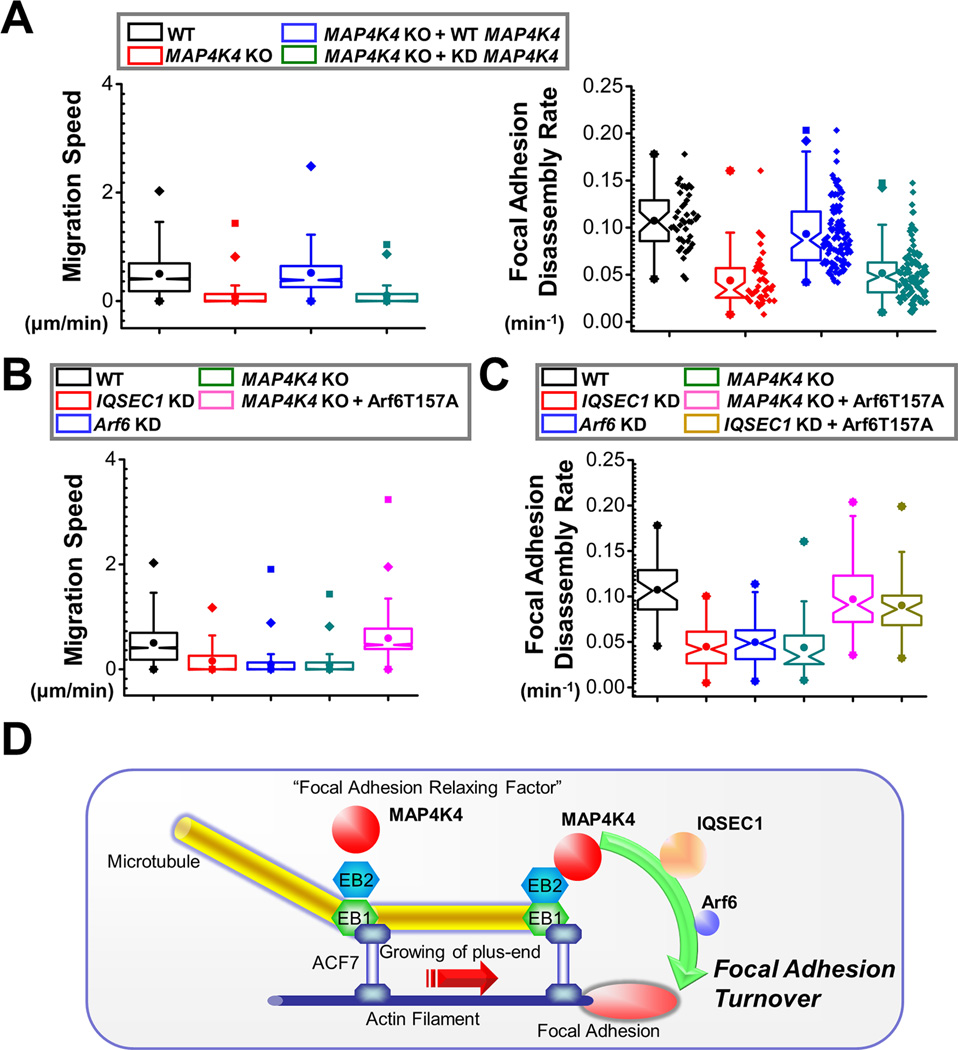
Figure 7. MAP4K4 and IQSEC1 interaction regulates FA dynamics and cell motility.
(A) Cell motility and FA dynamics were analysed for WT, MAP4K4 KO cells, and KO cells rescued with WT MAP4K4 or MAP4K4 KD mutant. For cell motility assay (left panel), N= 30 cells × 120 time points for each group. P<0.01 between WT and MAP4K4 KO, MAP4K4 KO and MAP4K4 KO + WT MAP4K4, and MAP4K4 KO + WT MAP4K4 and MAP4K4 KO + KD MAP4K4. For FA disassembly (right panel), N>40 for each group. P<0.01 between between WT and MAP4K4 KO, MAP4K4 KO and MAP4K4 KO + WT MAP4K4, and MAP4K4 KO + WT MAP4K4 and MAP4K4 KO + KD MAP4K4. (B, C) Quantifications of migration velocities (B) and FA disassembly rate (C) for control, IQSEC1-knockdown cells, Arf6-knockdown cells, MAP4K4 KO cells, and cells rescued with Arf6 T157A. For cell motility assay, N= 30 cells × 120 time points for each group. P<0.01 between WT and IQSEC1 KD; WT and Arf6 KD, WT and MAP4K4 KO, and MAP4K4 KO and MAP4K4 KO + Arf6 T157A. For FA disassembly, N>40 for each group. P<0.01 between between WT and IQSEC1 KD; WT and Arf6 KD, WT and MAP4K4 KO, MAP4K4 KO and MAP4K4 KO + Arf6 T157A, and IQSEC1 KD and IQSEC1 KD + Arf6 T157A. (D) A working model summarizing the role of MAP4K4 in FA turnover and cell migration. We posit that MT dynamics are coordinated by cytoskeletal crosslinkers, such as ACF7 that guides MT growth toward FAs. MT interacting protein EB2 can bind and deliver MAP4K4 to FAs, where MAP4K4 can subsequently activate IQSEC1 and Arf6, leading to FA turnover and efficient cell movement.