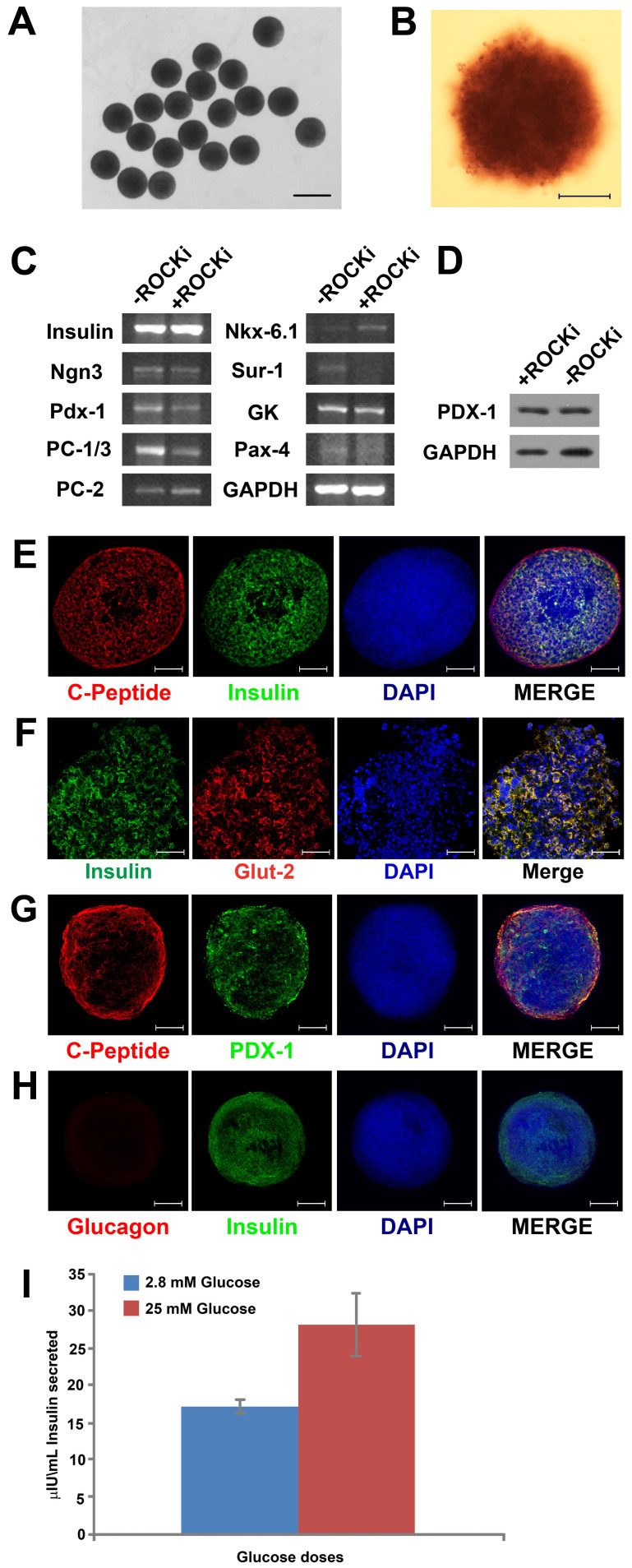
Figure 6. Differentiation of hiPSC hEBs into insulin-secreting cells.
(A) When treated with the pancreatic differentiation protocol for 18 days, hEBs differentiated into islet-like clusters that appeared uniform in sizes and spherical; Scale bar = 1 mm; (B) Over 85% of the cells differentiated from hEBs (formed under no-ROCK-i condition) were pancreatic β-cells, as evidenced by the positive staining for Dithizone (DTZ) in dark crimson red; Scale bar = 200 µm; (C) RT-PCR examination of the expressions of pancreatic lineage-specific genes by the cells after pancreatic differentiation; (D) Western blot analysis of PDX-1, another marker for pancreatic differentiation, in the cells; (E, F, G) Immunostaining of the cells revealed co-localization of insulin (in green) and C-peptide (in red), insulin (in green) and Glut-2 (in red), as well as C-Peptide (in red) and PDX-1 (in green); (H) Co-staining for Glucagon (in red) and Insulin (in green) revealed the absence of glucagon in insulin-secreting cells. Cell nuclei were stained in blue with DAPI. Scale bar = 50 µm; (I) ELISA for insulin secretion assay indicated glucose-responsive insulin secretion from the differentiated cells in a physiologic manner.