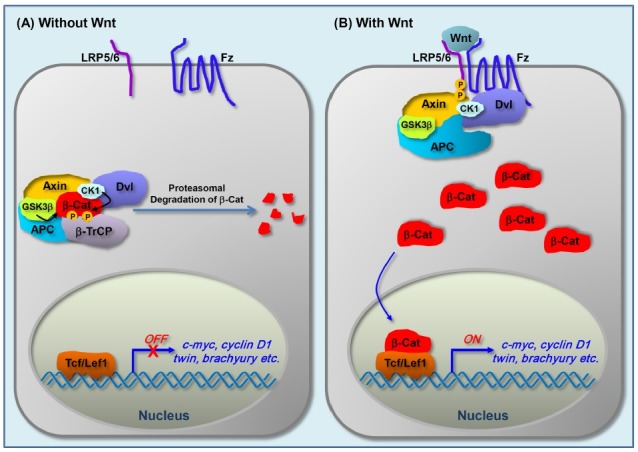
Fig. 1. Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Schematic diagram for the core components and signal transduction of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. (A) In the absence of Wnt, GSK3β and CK1 phosphorylate β-catenin degradation complex which includes APC and Axin. The phosphorylated β-catenin is recognized by β-TrCP and subsequently degraded by proteasomal pathway. As a result, TCF/LEF1 suppresses the expression of target genes. (B) In the presence of Wnt, binding of Wnt to Fz and its co-receptor LRP5/6 leads to phosphorylation of LRP6. Axin, itself alone or whole β-catenin degradation complex including Axin, translocates to the phosphorylated LRP5/6, which leads to stabilization of cytoplasmic β-catenin. The stabilized β-catenin translocates into the nucleus and interacts with TCF/LEF1, which in turn enhances the expression of target genes.