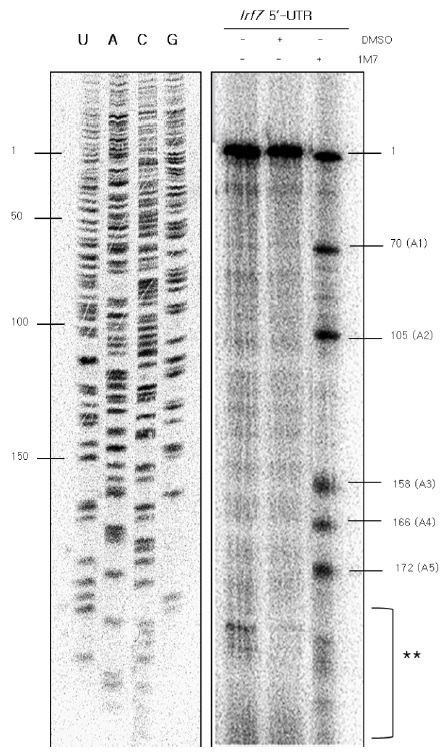
Fig. 2. SHAPE modification led to the identification of five distinct acylation sites in the Irf7 5’-UTR. For SHAPE, the Irf7 5’-UTR transcript was chemically modified using 1M7, dissolved in DMSO at pH 8.0, under denaturing conditions. The Irf7 5’-UTR mRNA was treated with 1 μl of 50 mM 1M7 dissolved in DMSO or 1 μl of DMSO. cDNAs were generated up to the acylation sites at 42℃ for 2 h using a [γ-32P]ATP-labeled probe and then loaded onto a 15 % denaturing urea-acrylamide gel. The single-stranded acylation regions were analyzed using a USB sequencing ladder. The location of the mRNA was deduced from the cDNA. The presence of the SHAPE reagent 1M7, and DMSO of Irf7 5’-UTR are indicated by the ‘+’ in each lane. The first lane was treated with neither DMSO nor 1M7. The second lane was treated with only the solvent, DMSO. The third lane was treated with the SHAPE reagent 1M7. The locations of the nucleotides and the acylation sites are marked on the left and right side of the gel, respectively. The first and second lanes were used as controls for the SHAPE reactions. The sites marked with “1” and double asterisks were excluded from the single-stranded region following SHAPE modification. The site marked “1” represents the size of the whole mRNA, and the asterisk-marked region was also seen in controls. All five single-stranded reactions occurred at adenosine residues.