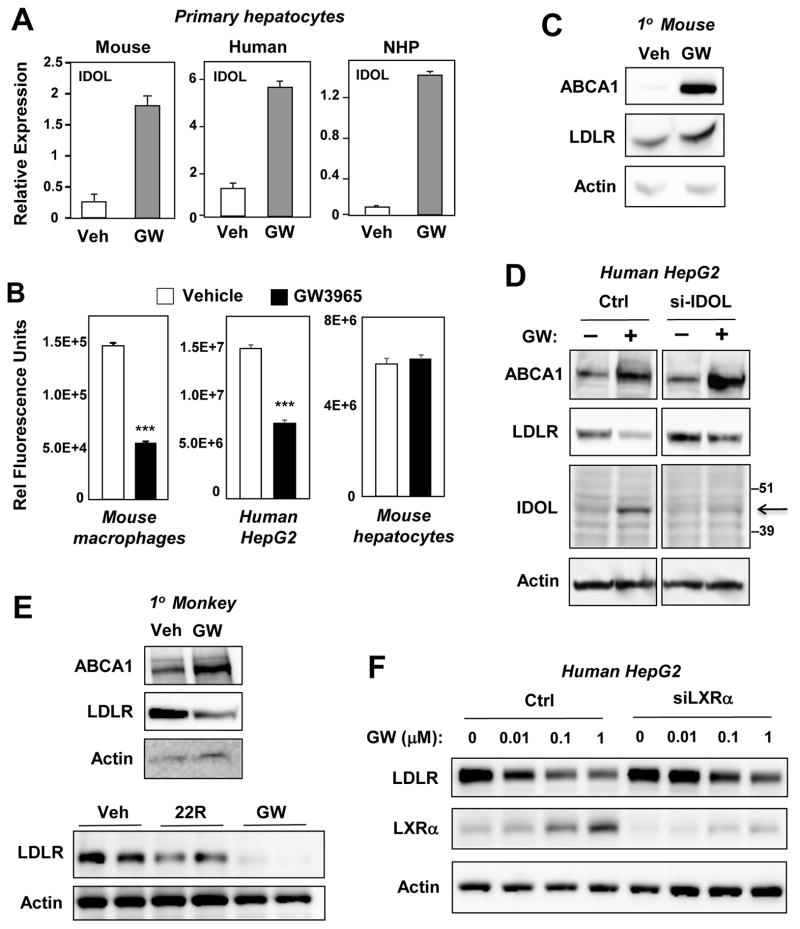
Figure 2. Species-specific regulation of hepatic LDLR protein expression by the LXR–IDOL pathway.
Primary hepatocytes from mice, humans, and nonhuman primates were serum-starved and treated with GW3965 (1 μM) for 24 h. (A) Regulation of IDOL mRNA expression by LXR agonists. (B) Quantification of cellular uptake of DiI-LDL uptake in the presence or absence of GW3965. Cell-associated fluorescence was measured with a Typhoon Instrument. n=3. ***P< 0.001. (C,D) Immunoblot analysis of protein lysates from primary mouse hepatocytes (C) or human HepG2 cells (D) treated with GW3965 (1 μM) for 24 h. (E) Immunoblotting of protein lysates from cynomolgus monkey hepatocytes treated with GW3965 (1 μM) or 22R-hydroxycholesterol (2.5 μM) for 24 h. (F) Immunoblot analysis of protein lysates from control or LXRα-siRNA-transfected HepG2 cells treated for 24 h with increasing doses of GW3965. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM.