Figure 4.
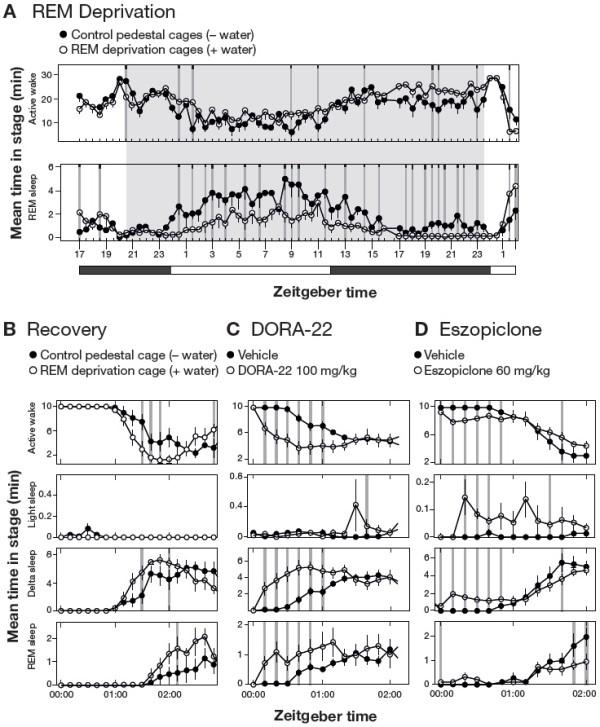
DORA-22 facilitates REM recovery following REM deprivation. A. REM deprivation in mice utilizing the pedestal method for 28 h (ZT 20:00 to ZT 24:00/00:00 on the subsequent day, n = 8 wild-type C57/BL6 mice in a balanced 2 × 1 day crossover). B. Sleep architecture at the cessation of 28 h of REM deprivation. Mice were alternately housed in cages containing pedestals and either no water (control condition, closed symbols) or water (REM deprivation condition, open symbols) in a balanced 2 × 1 day crossover as described in Methods (n = 8 wild-type C57/BL6 mice). Time spent in the indicated sleep stages immediately upon cage change to normal bedding (ZT 00:00, or lights-on) is shown. C. Effects of DORA-22 treatment (100 mg/kg p.o., open symbols) relative to vehicle (vitamin E TPGS, 20% solution, orally, closed symbols) on sleep architecture when administered coincident with the cessation of REM deprivation (ZT 00:00, n = 11 wild-type C57/BL6 mice in a balanced 2 × 1 day crossover in which each animal alternately received vehicle and DORA-22). D. Effects of eszopiclone treatment (60 mg/kg p.o., open symbols) relative to vehicle (vitamin E TPGS, 20% solution, orally, closed symbols) coincident with the cessation of REM deprivation (ZT 00:00, n = 11 wild-type C57/BL6 mice in a balanced 2 × 1 day crossover in which each animal alternately received vehicle and eszopiclone). Significant differences are indicated by gray vertical lines, and black tic marks indicate significance level (short, medium, long, P < 0.05, 0.01, 0.001).
