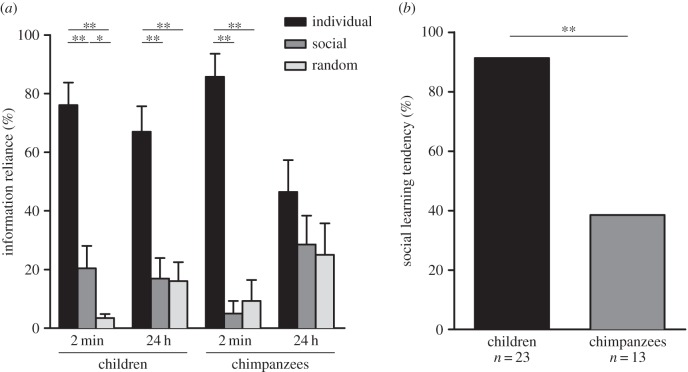
Figure 2.
Children rely more on social information than chimpanzees do. (a) Mean (+s.e.m.) information reliance for the children and chimpanzees across both time-delay conditions as a percentage, and (b) percentage of children and chimpanzees who explored the location that had been observed to be rewarding for a conspecific during their first individual trial. One asterisk, p < 0.05; two asterisks, p < 0.01.