Figure 6. Overexpression of WT A10 PABPN1 protects against age- and muscular dystrophy-related dysphagia.
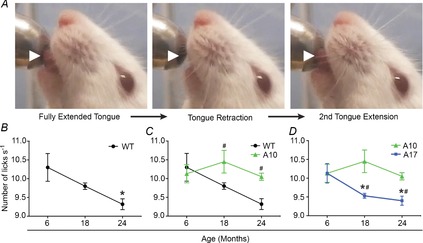
A, single lick episode is depicted using still frames from a representative lick assay video. White arrowheads highlight the extension and retraction of the tongue. B–D, quantification of lick rates of WT, A10-WT or A17-MUT mice at 6, 18 and 24 months of age. Data are means ± SEM from 3 to 13 mice. B, WT lick rates significantly decreased at 24 months of age (*P < 0.05). C, overexpression of WT A10 PABPN1 provided a protective effect on lick rates at both 18 and 24 months of age (#P < 0.05) when compared to WT mice at these time points. Data from WT and A10-WT mice. D, lick rates of A17-MUT mice significantly decreased at 18 and 24 months of age (*P < 0.05) and were significantly impaired at these time points compared to A10-WT mice (#P < 0.05). A10-WT, wild-type A10.1 PABPN1 overexpression transgenic mouse; A17-MUT, mutant A17.1 PABPN1 overexpression transgenic mouse; PABN1, polyadenylate binding nuclear protein 1; WT, wild-type.
