Fig. 1.
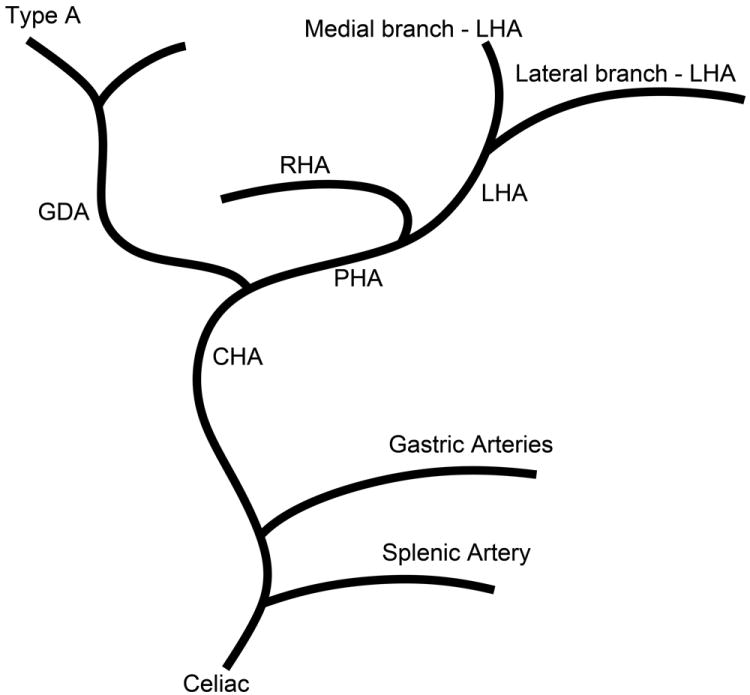
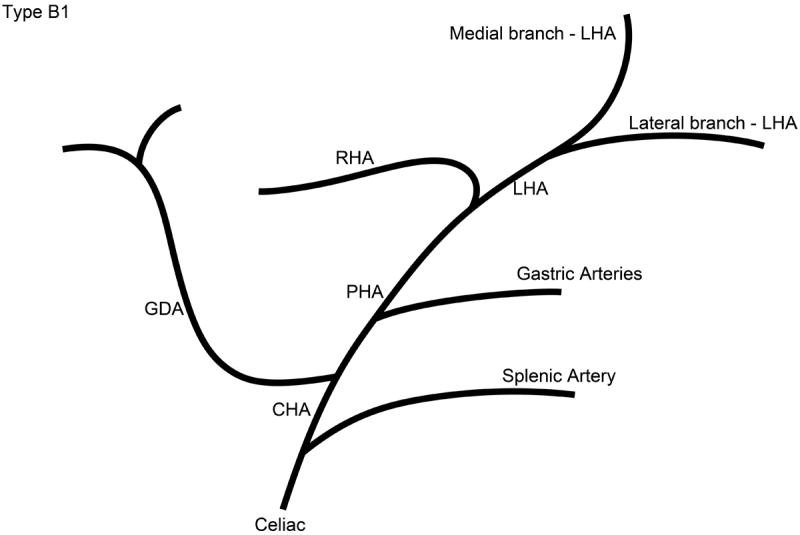
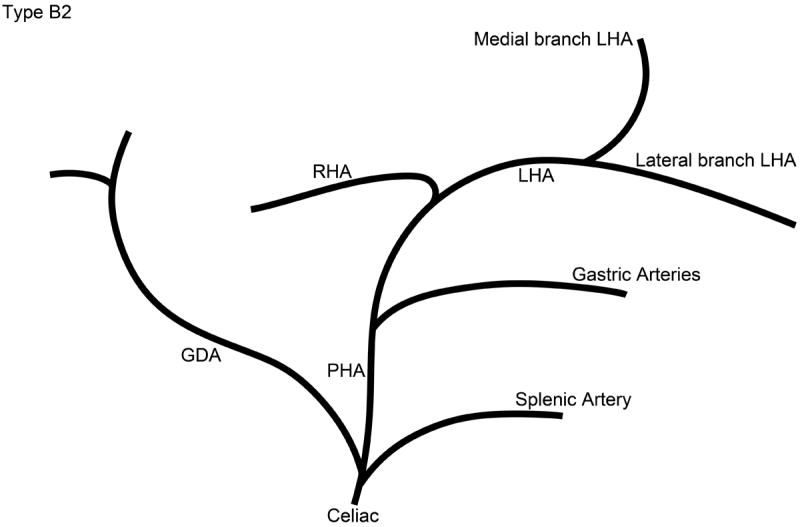
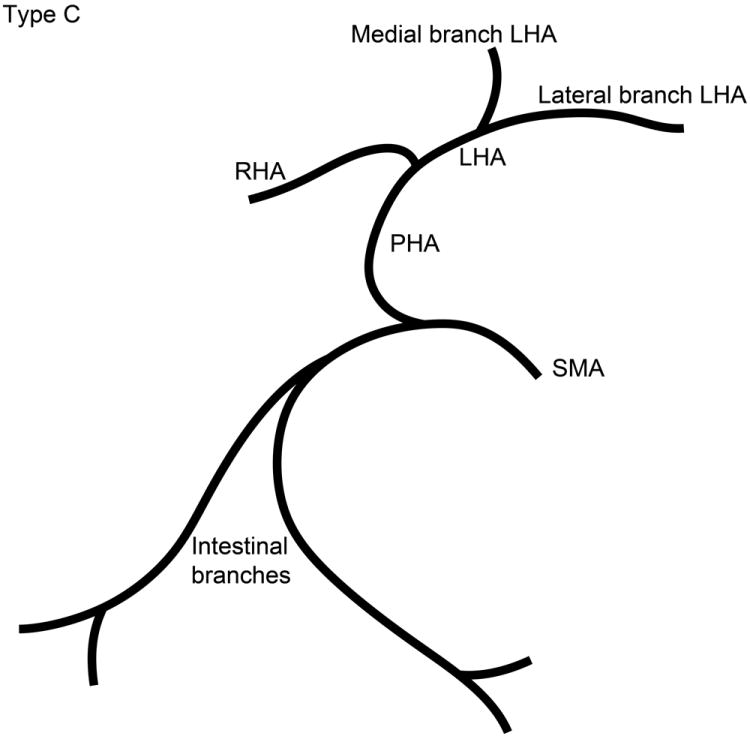
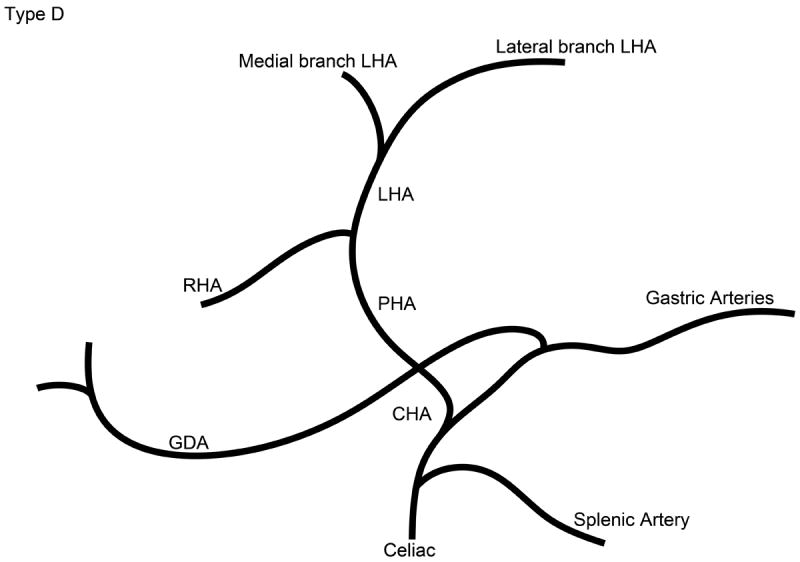
Schematic representation of the five different branching patterns of the rabbit celiac axis. (A) Type A is the most common branching pattern and characterized by the gastroduodenal artery (GDA) arising off the distal portion of the common hepatic artery (CHA) and all gastric arterial branches arising off of the CHA. (B) Type B1 is characterized by the GDA arising off the proximal portion of the CHA and gastric arterial branches arising from both the CHA and the proper hepatic artery (PHA). (C) In Type B2, the CHA cannot be clearly identified as a distinct segment and represents a trifurcation of the celiac axis into the splenic/gastric arteries, the CHA and the GDA. Gastric arterial branches may also arise from the PHA. (D) Type C represents the variation where the PHA arises from the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) and not the celiac axis. (E) Type D represents the variation where the GDA does not arise from the CHA, instead coming off of a gastric arterial branch.
