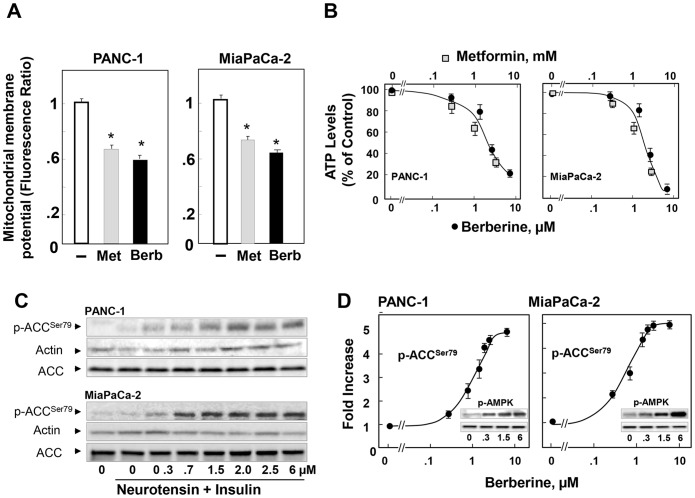
Figure 3. Berberine and metformin induce mitochondrial membrane depolarization, reduce ATP levels and activate AMPK in PDAC cells.
A, Cultures of PANC-1 and MiaPaca-2 cells were incubated in the absence or in the presence of 3 µM berberine (Berb) or 1 mM metformin (Met) for 17 h in DMEM containing 5 mM glucose. The change in mitochondrial membrane potential was measured using the mitochondrial membrane potential indicator JC-1. The results are expressed as an average ratio of red/green florescent intensity in a single visual field (mean ± SEM). At least 5 fields were studied in each condition. P values were determined using the t-test (SigmaPlot 12.); *p<0.002. B, Cultures of PANC-1 and MiaPaca-2 cells were incubated in the absence or in the presence of berberine or metformin at the indicated concentrations for 17 h in DMEM containing 5 mM glucose and 2.5% FBS. C, Cultures of PANC-1 (upper panels) and MiaPaCa-2 (lower panels) were incubated in the absence or in the presence of berberine at the indicated doses for 17 h. Then, the cells were stimulated for 1 h with 5 nM neurotensin and 10 ng/ml insulin and lysed with 2X SDS-PAGE sample buffer. The samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies that detect the phosphorylated state of Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC) at Ser79. Western blotting for actin was used to verify equal loading in the same membrane and a separate gel confirmed that expression of total ACC protein was not changed by any of the treatments. D, Quantification was performed using Multi Gauge V3.0. The values represent the mean ± SEM; n = 3, fold increase in ACC phosphorylation at Ser79. Inset, phosphorylated state of AMPK at Thr172 at the indicated concentrations of berberine (µM).