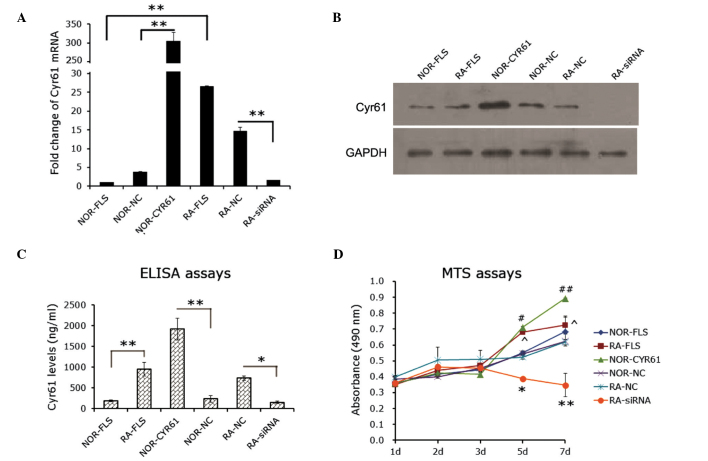
Figure 2.
Role of Cyr61 in FLS cell proliferation. (A) Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction evaluation for the efficacy of Cyr61 siRNA or cDNA transfection in FLS cells. The mRNA level of Cyr61 in normal FLS cells was used as a control. **P<0.01. (B) Western blotting evaluation for the efficacy of Cyr61 siRNA or cDNA transfection in FLS cells. Cyr61 (40 kDa) was detected using a mouse IgG1 monoclonal antibody specific for Cyr61. GAPDH served as the loading control. (C) Detection of levels of Cyr61 secreted into the culture medium using enzyme-linked imunosorbent assays. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01. (D) MTS assay detection of cell proliferation. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments conducted in triplicate. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, compared with RA-NC; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01, compared with NOR-NC; ^P<0.05, compared with NOR-FLA. RA, rheumatoid arthritis; FLS, fibroblast-like synoviocytes; siRNA, small interfering RNA; NOR-FLS, normal FLS cells; NOR-CYR61, normal FLS cells transduced with lentivirus vector encoding Cyr61 cDNA; NOR-NC, normal FLS cells transduced with control lentivirus vector; RA-NC, RA-FLS cells transfected with control siRNA; RA-siRNA, RA-FLS cells transfected with Cyr61-siRNA.