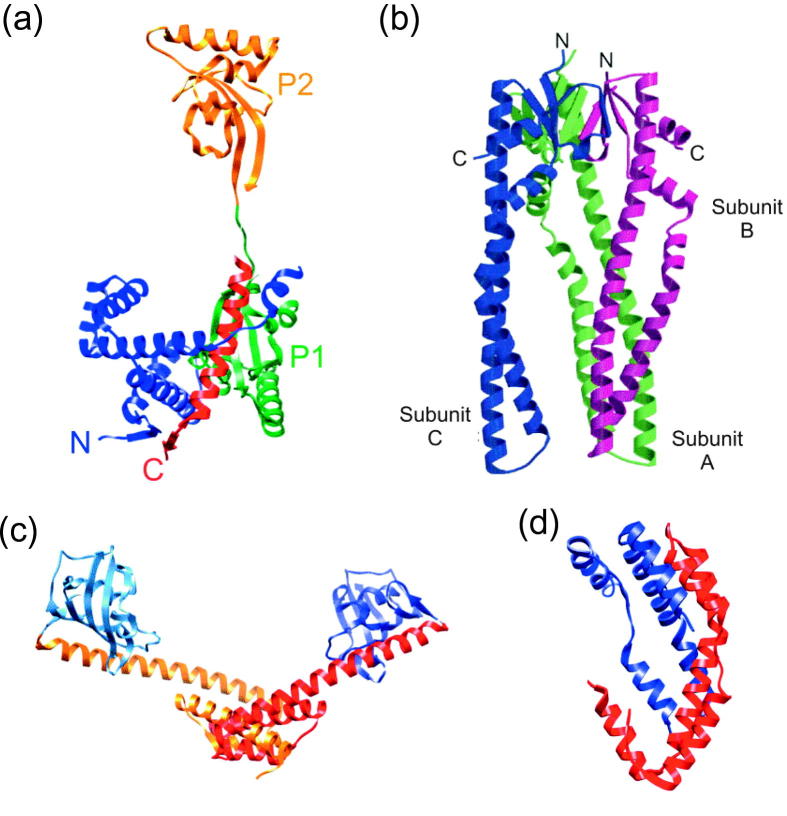
Fig. 5.
Crystallographic structures of selected periplasmic chaperones. (a) Ribbon diagram of SurA coloured as follows N-terminal domain (blue), PPIase domain P1 (green), PPIase domain P2 (orange) and C-terminal domain (red) (1M5Y [80]). (b) Ribbon diagram of Skp trimer with the subunits A, B and C coloured in green, magenta and blue, respectively, (1U2M [104]). The tips of the α-helices in subunits A and B have been modelled. (c) Ribbon diagram of the FkpA dimer showing the N-terminal chaperone domains (red and orange) through which dimerisation occurs and the C-terminal PPIase domains (blue) (1Q6H [109]). (d) Ribbon diagram of the Spy dimer with the monomers coloured individually in red and blue (3O39 [114]). (a), (c) and (d) were generated from PDB files using the accession numbers given in brackets using UCSF Chimera molecular visualisation application [236]. (b) was reproduced from [104] with permission from Elsevier, © 2004.