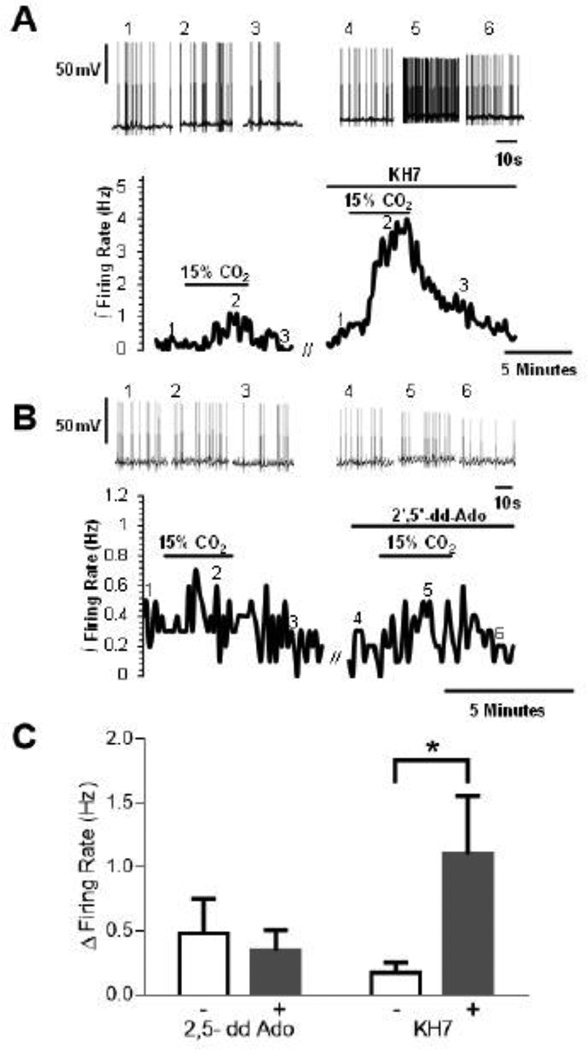
Figure 6.
The effects of sAC and tmAC inhibition on the magnitude of the chemosensitive response in LC neurons from neonatal rats older than P10. The inhibition of sAC enzyme by KH7 (30 µM ) causes an increase in the firing rate response induced by hypercapnia while the inhibition of tmAC by ddAdo (30 µM) has not effect on the firing rate rate response induced by hypercapnia. (A) A typical chemosensitive response for whole cell current clamp experiments from neonatal rats older than P10 when CO2 is increased from 5 to 15% and the effect of KH7 on that increased firing rate response. The bottom trace represents the integrated firing rate (reported as Hz measured in 10 s bins). Note that 15% CO2 causes a small increase in the integrated firing rate of LC neurons that is reversible upon return to 5% CO2. This increase is dramatically increased in response to 15% CO2 in the presence of the specific sAC inhibitor KH7. The top trace shows individual action potentials (voltage scale of 50 mV) at a faster time scale than the lower panel. The first three sets of action potentials depict the action potentials at the points indicated by the numbers on the lower trace (1, 2 and 3) for the control response. The second three sets of action potentials depict the action potentials at the points indicated by the numbers on the lower trace (4, 5 and 6) for the firing rate response to hypercapnia in the presence of KH7. (B) A similar set of traces to (A) but for the effects of the tmAC inhibitor 2’,5’-dd-Ado. In the lower trace, note that hypercapnia induces a small increase in firing rate that is similar in both the presence and in the absence of 2’,5’-dd-Ado. The upper traces show individual action potentials segments at the times indicated on the lower traces but at a faster time scale. (C) Bar graphs showing the mean ± SEM for the change in firing rate in going from 5% CO2 to 15% CO2 in the absence vs. the presence of 2,5-dd Ado (left two bars; n=5)) and in the absence vs. the presence of KH7 (right two bars; n=6). Note that 2’,5’-dd-Ado does not affect the firing rate response to hypercapnia in LC neurons but that KH7 results in a significantly higher (P<0.05) response of firing rate to hypercapnia.