Figure 2.
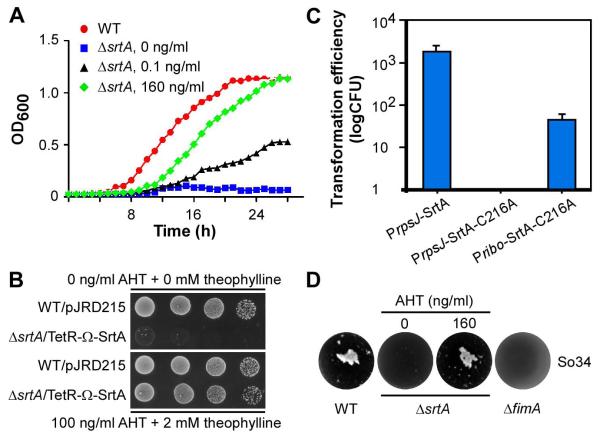
The housekeeping sortase srtA of A. oris is an essential gene. (A) A conditional mutant of srtA (ΔsrtA) was generated by deleting the chromosomal srtA gene in the presence of the plasmid pTetR-Ω-SrtA expressing SrtA under the control of a tetracycline-inducible promoter in combination with a riboswitch element. Growth of this mutant in the absence (square) or presence of anhydrotetracycline (AHT; 0.1 ng/ml, triangle or 160 ng/ml; diamond) and 2 mM theophylline was monitored by optical density (OD600) and compared to that of the wild-type MG1 strain harboring an empty vector (pJRD215; circle). (B) Ten-fold serial dilutions of overnight cultures of the wild-type MG1 and the conditional ΔsrtA strains in A were spotted on agar plates with and without inducers AHT and theophylline. Cell growth was recorded after 3 days of incubation at 37°C with 5% CO2. (C) Individual plasmids expressing SrtA or SrtA-C216A were electroporated into the MG1 strain. PrpsJ indicates that expression of SrtA is under the control of the strong rpsJ promoter, whereas Pribo refers to a weaker promoter. Transformation efficiency was determined as colony-forming unit (CFU) per microgram of DNA. The results are presented as an average of three independent experiments; each done in triplicates. (D) Interbacterial interaction between S. oralis 34 and the wild-type MG1, fimA deletion mutant, or srtA depleted mutant strain was determined by coaggregation assays.