Figure 4.
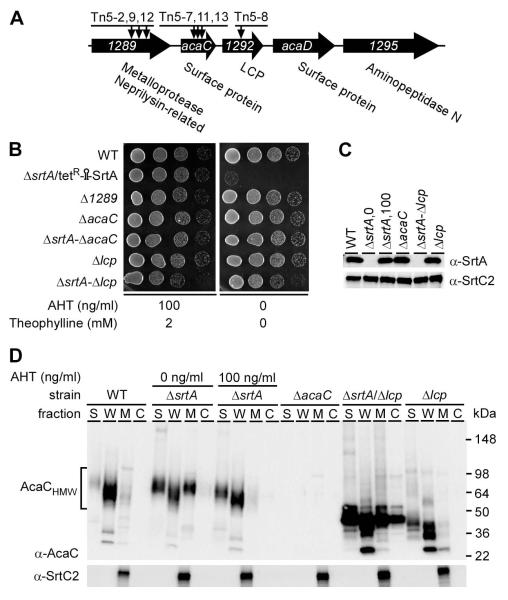
acaC and lcp are genetic suppressors of srtA. (A) Shown is a graphic representation of the acaC gene locus in the chromosome of A. oris MG1. This locus encodes two surface proteins, a metalloprotease, an aminopeptidase, and a LytR-CpsAPsr (LCP) family protein. Arrows indicate the insertion sites mapped in Tn5 mutants. (B) Cell growth of the MG1, conditional srtA deletion mutant, and various non-polar deletion mutant strains was observed on agar plates in the presence or absence of inducers as described in Fig. 1B. (C) Membrane fractions of various A. oris strains were collected and subjected to western blotting with antibodies against SrtA (α-SrtA) or SrtC2 (α-SrtC2). Numbers 0 and 100 indicate the concentration (ng/ml) of AHT supplemented in the culture of the conditional srtA mutant. (D) Cells of various strains grown to mid-log phase were normalized by optical density. For the conditional srtA deletion mutant, cells were grown in HI broth containing 1% AHT before subcultured in fresh media without (0 ng/ml) or with (100 ng/ml) AHT and 2 mM theophylline. Culture supernatant (S), cell wall (W), membrane (M), and cytoplasmic (C) fractions were obtained by cell fractionation. Equivalent protein samples were separated on 4-12% Tris-Glycine gradient gels and detected by immunoblotting with antibodies against AcaC (α-AcaC) and SrtC2. Molecular mass markers in kDa and high molecular weight AcaC proteins are shown.